The Homo sapiens
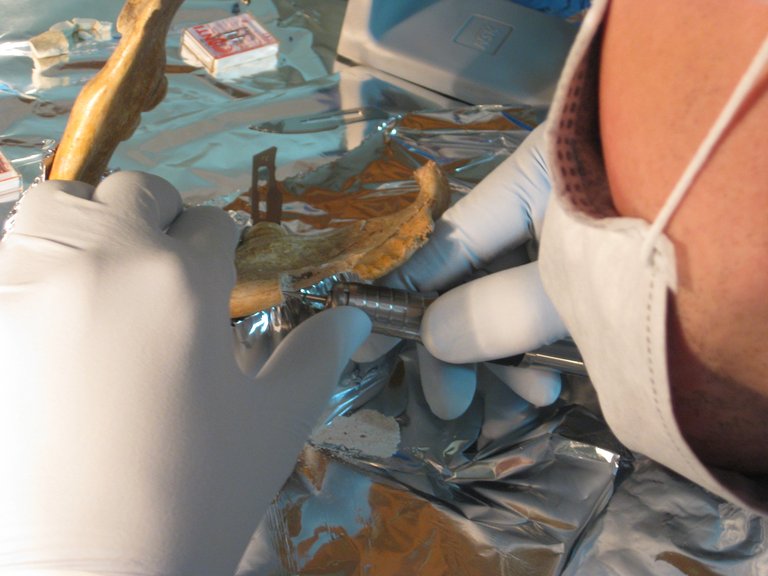

Researchers from the Harvard Medical School and the Max Planck Institute of Evolutionary Anthropology have presented the genetic analysis of a man's marriage of 40,000 years ago. It is a fossil of Pe0.000 tera cu Oas in Romania, cave with bones in Romanian, whose DNA contains the largest proportion of the Neanderthal genome that has been found in a Homo sapiens: Between 6.0 and 9.4%. Thus, the researchers conclude that their last Neanderthal ancestor was only 4 to 6 generations: 200 years maximum.
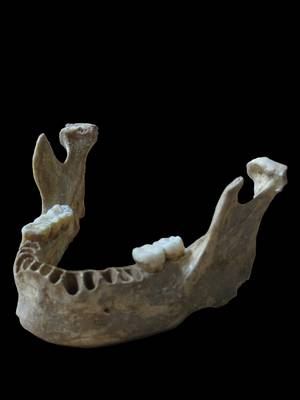
The Oase 1 is called this way, the discovery in Europe is one of the oldest fossils of the Homo sapiens. It is between 37,000 and 42,000 years old, dating directly to the Carbon-14, and although morphologically modern, it also has features consistent with its Neanderthal origin. Now, genetic analyses by Svante Pääbo's group have shown that Neanderthal was in greater proportion than any other Homo sapiens.
At present, all human populations other than sub-Saharans retain the genome of Neanderthal origin, between 1 and 3%. This means that in the past Neanderthals and our ancestors hybridized out of Africa and populate Eurasia. Through genetic studies, anthropologists have calculated the time when the crossing occurred, which was initially between 37.000-86.000 years ago and which has recently been more limited by the other two fossils found in Western Siberia and Eastern Russia, in a period of between 50,000 and 60,000 years. Likewise, according to the discoveries made so far, it could be produced in the corridor from Africa to Eurasia, in small proportion and in a limited period.
However, the fossil Oase 1 places hybridization in Europe, about 40,000 years ago, that is, much later than was thought. Also, because genetic study suggests that the fossil Oase 1 has a Neanderthal contribution that seems older, that is, the individual was the successor of a line of Homo sapiens previously hybridized with the Neanderthals.
To carry out the analysis, researchers at the Max Planck Institute have extracted and analyzed two 25 and 10 mg jaw samples respectively. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA has been analyzed and data from as many others, both current humans and human fossils have been used. Finally, to calculate the number of previous generations in which hybridization occurred, the length of the fragments of sequence of Neanderthal origin has been measured. The longer the fragments are, it means that less times the recombination of DNA has occurred, so few generations have passed between the individual who made their genetic contribution and the one who is investigating. In this case, the parts are so long that anthropologists have calculated a difference between four and six generations between the oldest Neanderthal ancestor and the Oase 1 Homo sapiens.
As for other partners, they conclude that it has a closer relationship with the current inhabitants of East Asia and of American origin than with the current Europeans. In the same cave was also discovered the fossil of a human skull in later excavations, Oase 2, and in the article of Nature it has been mentioned that “it also has the morphological characteristic of having been hybridized with Neanderthals and that could be of the same time”. As genetic studies of more individuals increase, we will know more clearly the complex population of Eurasia.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian








