The way of the blood
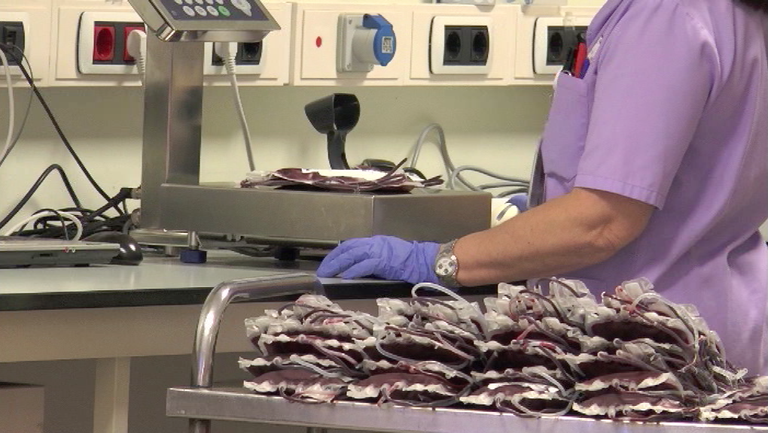
OFF by: We are located in Galdakao, Basque Transfusion and Human Tissues Centre. This is where all the blood that is donated every day in Álava, Gipuzkoa and Bizkaia arrives. The blood is processed and the components are obtained for later use in transfusions.
in less than 24 hours, all this blood will be ready for use.
FROM THE COURT:Miguel Angel Vesga, director of the center
"In the Autonomous Community of the Basque Country, about one hundred thousand blood donations are required per year, that is, about 400 to 500 a day. Divided into components, we produce 300,000 products a year and about 50,000 people receive them."
OFF by: The blood reaches the processing unit twice a day, at noon and at night. Here the blood is divided into components, which are treated and stored before being distributed to community hospitals.
FROM THE COURT:Miguel Angel Vesga, director of the center
"These are some of the units delivered yesterday. This is a normal bag, 400 cubic centimeters of blood, and it is attached to several other bags."
OFF by: They collect the components in these bags in a fully automated manner. In these machines the ingredients are distributed under sterile conditions, making the most of each product.
THE ANIMATION
OFF by: Blood has four main components and three are used for transfusions.
Red blood cells or red blood cells are transferred to normal transfusions: operations, transplants, wounded...
Platelets are clotting cells and are usually collected by cancer patients or those with hematological problems.
Plasma, a liquid component, is not used directly. Medicines such as albumin, immunoglobulins or clotting factors for hemophiliacs are produced from plasma, among many others.
White blood cells are discarded.
FROM THE COURT: Verónica Campaña, laboratory technician: "Explanation of how the centrifuge works, in situ."
OFF by: After exiting the centrifuge, the bags are separated. Hereinafter, each component is processed separately.
The red blood cells are filtered to remove any remaining white blood cells. The health of the recipient may be compromised by white blood cells, so all components are irradiated to ensure that all white blood cells have been destroyed.
After processing, the products are weighed, recorded and stored.
The red blood cells are stored in the refrigerator in grade 4.
The plasma undergoes two freezing processes. It is then shipped out for the production of derived drugs.
Platelets accumulate in these trays in motion at 22 degrees. With continuous movement, the platelets do not adhere to each other and deteriorate.
FROM THE COURT:Miguel Angel Vesga, director of the center
"They're living cells, it's not an inert product. They must retain all properties when the patient receives them. The blood must be treated finely from the moment it is taken out until it is received by the recipient."
OFF by: The information of each blood donation and the products derived is also treated finely. The traceability must be absolute.
FROM THE COURT:Miguel Angel Vesga, director of the center
"Blood donation is voluntary, unpaid and, very importantly, anonymous. The recipient does not know the origin of the products received, but we must know." (...)
To the OFF: Each product has a code that is maintained throughout the entire donor to recipient chain. In addition, a record is kept of the people involved in each step of the process, from the selection of the donor to the transfusion of the product.
OFF by: To ensure traceability, they have access to a complex computer system. The system receives in real time what is happening with each donor, recipient and component.
At this time, for example, it is quarantined for freshly processed blood components. They must be approved by the analysis laboratory.
2. [PLATELETS AND APHERESIS]
OFF by: Of the three components that are acquired from the blood, platelets, plasma and red blood cells, platelets are the ones that cause the most headaches. They are the most expensive to produce and the fastest to expire.
FROM THE COURT: Miguel Angel Vesga, director of the center
"This is a dose of platelets... Platelets are essential to support oncology treatments... They have the distinction of having a very short expiration date, only five days, and five normal blood donations are required to obtain a full dose.
We'd get these platelets out of a bag of blood; and a full dose is obtained by putting together five times as many. This is the dose that the patient will receive, this one that goes in this bag."
FROM THE COURT: Assisted by Miguel Angel Vesga
To the OFF: There are several reasons why platelets are an expensive product. On the one hand, they are fragile. On the other hand, since five small bags are required to obtain a dose, more sterile material is consumed.
“And especially with the expiration period so short, three, four, five days, the chances of losing the product are higher.”
OFF by: In order to improve platelet management and reduce the expiration rate, the Basque Centre for Transfusion and Human Tissues has turned to mathematicians...
OFF by: Based on actual platelet production and consumption data, the UPV/EHU Mathematical Technology Transfer Group has constructed a model. The model proposes the number of platelets that should be produced each day of the year.
SECTION: Mathematicians
OFF by: Thanks to this model, less platelet extinction has been achieved. So far, the extinction rate was 15%.
OFF by: One possibility to obtain a higher number of platelets is to administer blood by apheresis. With this system, a full dose of platelets is obtained each time blood is administered.
FROM THE COURT: IRUNE ETXEBARRIA, nurse. "It's a donation by apheresis..."
OFF by: The administration of blood by apheresis requires more complex than conventional devices and is slower: the donor must be between one and one and a half hours old. Currently, just under 10% of the blood is administered by apheresis. However, it has important advantages.
FROM THE COURT: Assisted by Miguel Angel Vesga
"It has a very good side. Higher amounts are obtained, yes, but above all it allows to obtain very precise and special ingredients for specific patients. We know the blood of these donors in great detail and for patients with special needs it is easier to get products with apheresis."
3. ANALYSIS AND DEMANDS
OFF by: Each blood bag arrives together with three sample tubes. All donated blood is systematically analyzed at the General Laboratory of the Transfusion Center. Possible infections are sought and the group to which the blood belongs is determined.
FROM THE COURT: MARIA AZKARATE, doctor. "This machine sorts the pipes. Before it was done by hand, and it was 1,500 tubes a day..."
FROM THE COURT: Miguel Angel Vesga, director
"All donated blood is analyzed, always, no matter how many times a person has donated blood. There are three types of tests.”
To the OFF: One type of test detects viruses directly if there is a copy of them: mainly hepatitis B and C viruses, and HIV viruses.
A second set of tests looks for infectious diseases, but with the detection of antibodies. These tests tell if the donor has been in contact with these diseases, and here again, hepatitis and HIV are sought. In some cases, additional tests are performed to rule out the possibility that the donor has traveled to epidemiologically dangerous regions: malaria, Chagas disease...
OFF by: The donor screening system allows the laboratory to exclude very little blood. Almost 99% of donated blood units are usually good.
OFF by: The third type of analysis determines which group the donor's blood belongs to.
CUT: Miguel Angel Vesga
"The blood of the donor and the recipient must be compatible. Not only with respect to the A B Zero and Rh groups. Many other blood cell systems or groups must also be respected."
OFF by: These blood systems or groups depend on about 30 antigens. These molecules are expressed on the surface of red blood cells and, in combination, form 600 possible clusters. Most of us are members of normal blood groups, but not all. These people work independently.
CUT: Miguel Angel Vesga
"Some people have very special groups that are rarely given. And if they ever needed a transfusion, it would be difficult to find blood for them; it is difficult to have compatible blood for them in the store."
To the OFF: When they find one of these special people, they ask him to donate blood, which they store in the transfusion center, frozen under very special conditions, for at least 20 years. This way, these people, or others with a similar genetic profile, will have access to compatible blood if they need a transfusion.
OFF by: Like everything else, orders are prepared in an automated manner.
CUT:EBE ZEANURI, laboratory technician. "We enter the data into the system and he tells us which bag to take..."
OFF by: Each hospital has stock for 3-5 days. Enough to deal with an emergency situation on their own. All this stock is also controlled from Galdakao. The goal is to prevent these valuable products formed from donated blood from expiring in a refrigerator.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian