Energy contained in water

Water from rivers and streams is used as a source of energy from the first century BC. Also in the Middle Ages hydraulic energy was the basis of industrialization. Currently, however, hydraulic energy is used to obtain electricity (hydroelectric power) by passing the water captured in the dam or reservoir through a turbine. This turbine drives alternators and therefore the kinetic energy of the water is transformed into electrical energy. The higher the amount of water and the speed of water, the more electricity the hydroelectric power plant will produce. When the installed power is less than 5,000 kVA they are called Small Hydroelectric Plants or Hydroelectric Minicentals. Most of them are built in Euskal Herria.
As for history, Euskal Herria, XIX. In the 20th century many companies built their own power plant to obtain electricity. This trend was strengthened and generalized in the early years of this century. But large companies using large reservoirs and dams, low oil prices and high costs of these small power plants caused small hydroelectric power plants to stop being built from the 1960s, and many of those operating closed one after the other. In recent years, however, the oil crisis and, to some extent, the impulse of alternative energies has reformed, automated and launched numerous of these small power plants, especially since the 1980s.
Some technical explanations
The Small Hydroelectric Plants can be of two types: the plants with slopes and the plants of foot of prey. The first collect water through a small dam of the riverbed or streams. The water then circulates through the ramp to the load chamber, from where it is directed to the turbine through the pressure tube. The load chamber is necessary to prevent air entering the pressure pipe, which would generate excessive pressure. Once the water passes through the turbines, it is released in the place to the river or stream. The post dam plants are built in large reservoirs intended for electricity generation or other uses in the lower part of the dam. In these cases the water is collected to the dam and inserted directly into the pressure pipe. Then, as on previous occasions, it passes through the turbines and goes to the channel.
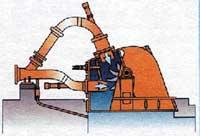
It is clear that water is essential for the generation of hydroelectric power, but also essential, in addition to electricity generators, turbines that affect them. The turbines can be classified into two groups: the action turbines, which work for the water discharge speed, and the reaction turbines, the water pressure and the speed. In the small plants of our country are used those of the first group, which are usually of three types. Pelton turbines especially suitable for large jumps and relatively small flows. Kaplan turbines are suitable for small jumps (under 30 m) and large flows. Finally, Francis turbines that adapt to intermediate situations in the previous one can be used in a wide range of flow and water jump. However, to know the power to be installed with one or another turbine and the amount of energy that will occur throughout the year, it is necessary to know the flow of the river or stream at this point. This is done taking into account different parameters (precipitation, soil type, etc. ), but always with a long series of years to enter the dry, normal and rainy years. This data calculates the rated flow and flow rate (water flow in annual days) of the channel in each day. The latter will be subtracted from the ecological flow, that is, the minimum flow required by the channel throughout the year and Q80 and Q100 are calculated, that is, the existing flow between 80 and 100 days a year. With them you can know the number of days that each type of turbine would work and, therefore, choose the most suitable.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of hydroelectricity are remarkable. On the one hand, the energy conversion performance is very high, between 80 and 90%, and on the other, especially in small systems, the negative ecological impact is low. It is currently the simplest and cheapest way to obtain energy, being the most used in renewable energy sources.
In small plants, although their ecological impact is low, it exists. Although hydroelectric plants do not consume or pollute water, they hinder the migration of fish and the correct transport of food downstream, radically alter the dynamics of the river, drastically reducing the flow of water in some sections of the channel, altering the level of the groundwater layers and the composition of the packaged water. In cases where small dams are replaced by reservoirs, their construction produces great changes in the submerged territories, both ecological and social. In fact, where large dams and reservoirs are built, many of its inhabitants have to move to other places. The severity of these damage depends on the size of the work, being essential the correct application of corrective measures that are considered ecologically acceptable (adequate ecological flow retention, special structures for fish to overcome prey, etc. ).
Published in 7
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian








