Water saving devices

Earth is a “blue planet” in which water predominates. However, most of the water on Earth is in the sea (94% of the total). For drinking, watering, etc. We use fresh water. About 75% of the fresh water we use in the world is used by agriculture, while the rest is used to drink, wash and industry.
In the part of the Earth in which we live, in the Basque Country, fortunately there is no lack of water in general (remember that in the towns and cities we have all known and suffered water restrictions), it is clear that water is becoming an increasingly scarce and increasingly valuable good, which we can appreciate in the bill of water. Facing the future, in addition to scarce, and therefore increasingly expensive.
Therefore, we should act as in other products such as garbage. The three pillars so known in terms of waste, reduction, reuse and recycling, are also valid in water. Although the subject of this article is not the reuse and recycling of water, we must not forget the trials being carried out in some places in Europe (Germany, Sweden) for the reuse of water.
For example, in the restaurant of the Frankfurt Savings Bank, the water that is poured by the sinks is taken to a deposit for further use in the bathrooms. At the airport of the same city is used to collect rainwater and clean the bathrooms. And it is a luxury the water that has been purified to be able to drink, then the caca, the urine, the papers, etc. Use to drag.
However, although this type of sessions will be seen more and more often, the theme of this article is to show a way to reduce water consumption in homes and cities. The boards of the administration and the authorities to reduce water consumption in their own home are only taken into account in case of drought, since when the drought disappears we forget it. There are different devices on the market that can reduce water consumption. They are not very new, not complicated, not expensive, and very effective.
Unfortunately, however, we still know them and use them little. Even if it is not for ecological consciousness, it is also because they serve to save money. This article shows some devices of the brand RST, specialized in water saving systems, which is not the only brand of savings existing in the market.
Toilet economizer

This simple system will be installed in the bathroom water tank. In most toilets, pulling the handle, the internal valve of the tank opens and does not close until all the water comes out. For example, to carry 200 ml of urine 8, 10 or 12 liters of water are used. Although most of the tanks are drained completely, there are currently other tank systems on the market that allow saving water. In them, once pressed, the tank begins to empty, for the second time the valve is pressed and closed. But this system has a small problem: you have to know that it exists and use it (you have to press twice). Another “system” is to introduce a brick or other type in the tank, volume, so that the less water in the tank, but it will not be a solution for many.
The RST has a very simple system: it consists of placing two weights to the valve of the tank (two cylinders of stainless steel) by means of joints designed to the effect, so that it is pulled from the handle and the tank begins to drain, and when the handle is released, due to the weight of the steel cylinders, the valve will be closed before (3 liters of water of the toilet and 8 or 10 liters that enter the tank). It has two advantages over the normal tank: reduce the flow of water and reduce noise (which means a great comfort, especially at night: to fill the normal tank, and depending on the pressure, it takes 50/60 seconds, but with the saver only need 10/20 seconds).
Anti-faucet anti-faucet
This small saver is placed at the end of the faucet of sinks and sinks. The system sections are:
The main structure and the support of the elements is a chromed brass inner cylinder, threaded to be able to tie it to the faucet. Inside there are four coaxial elements: the first (in the direction of water) is the inner filter, followed by the propylene membrane, the diffuser and the outer filter. The inner filter is a very small eye network (0.25 mm). The water crosses the filter and is found with the propylene membrane, with a small screen to advance.
In this step two effects are produced: on the one hand, by forcing the water to pass through the mezzanine the flow of water is reduced; on the other, the water that does not enter the mezzanine collides against the membrane and moves backwards making a pump. As a result, a turbulence is generated in the section between the inner filter and the membrane, which continuously releases and moves the seams that have been trapped by water in a grid of 0.25 mm. In this way, the closure of the dirt network is avoided.

The water that has passed through the divider should continue for the tiny holes of the diffuser. Consequently, the water takes a great speed and is micronized, that is to say, it is “broken” in small micrometers (1 micrometer = 0.001 millimeters). Coming out of the diffuser, it is directed at full speed towards the outside filter, but in that interval it is mixed with the air, since between the brass cylinder and the filters there are slots to catch air. It receives the air from these cracks, that is, the moving water attracts the outside air (a high speed liquid generates depression around it, so it "absorbs" the surrounding air).
Once it leaves the diffuser and mixed with the air, the water must cross the outside filter before being expelled. The outer filter consists of three stainless steel concave meshes and large eyes (1.25 mm). The networks do not touch each other so that the lime does not accumulate, since thanks to this structure, once closed the faucet is poured the last drop and the lime does not accumulate in the filter (the lime accumulates in the filters by evaporating the water left in the filter when closing the faucet).
By micronizing the water and mixing with the air, it is possible to maintain the “quality” of the water jet with a much lower amount of water, that is to say, by placing the saver and opening the tap does not result in less water or having less strength, but, for example, we will realize that it takes longer to fill a container or sink.
Saving of shower
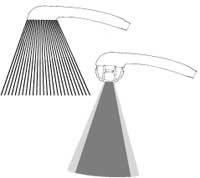
Its operation is similar to that of the faucet end. At the exit of the water there is a conical piece by which the water flow is reduced. Below is the diffuser with 3, 4 or 12 holes. When passing through the cone and diffuser the water accelerates and is micronized. In addition, between the diffuser and the cone, a turbulence is generated that prevents the adhesion of the lime. From the diffuser, the water absorbs the surrounding air and expels it mixed with the air, maintaining the quality of the water jet.
How much water saves?
Water saving is easy to know and everyone can do the test. First take the time (d1) needed for the faucet to fill the stack (or container) and then place the saver and perform the same test (d2). Thus, to calculate the percentage of water that is saved, just use the following formula:
Percentage of water saved =
= 100 - 100(d1/d2).

However, there are official tests carried out by the technicians. The following table shows the data of the official test carried out in 1995 by the Department of Industry and Energy of the Government of Catalonia (file number: 95009807). It is clear that despite the low water pressure it saves more than 50% on the faucet saver and more than 37% on the shower saver. The higher the pressure, the greater the savings (note that there are great variations in the pressure of water from one town to another or from one neighborhood to another or in the same building from the first to the last floor).
And how much money is saved?
When cold water is used, by saving water savings, the difference will be noticed on the water bill, but if the water used is hot, energy will also be saved, that is, the difference will be noticed on the water bill and on the energy bill (both electricity and gas). The economic saving is not predictable, since it depends on the way the water is used in each place, but it is clear that the greater the use of the water will be the saving and sooner the cost of saving will be recovered.
The attached table shows a practical example. However, and to make a general idea, it is necessary to know that the investment to make in a normal housing (a shower saver, two faucets economizers, one for sink and another for sink), is inferior to 15.000 pesetas (600 pounds) and the investment is amortized at the maximum in a year.
To finish
The water saving technology (and with it energy) is there, it is economical, efficient and without installation cost. In addition, it cannot be said that it is new. So, why is it used so little? We do not know. It might be necessary to make a promotional campaign from the administration, as was done with the low consumption light bulbs, but without waiting for it, why not try at home, at your bar, at your school, at your office or in your workshop?
For more information on water saving systems call 943 33 33 03.
SAVING WATER IN FIGURES (data from the Department of Industry and Energy of the Generalitat).
Saving Faucet RST
Pressure (kg/cm2) | 0.6% | 0.95 | 1,35 | 1,85 | 2,35 2,35 2,35 | 2,9 2,9 | 3,55 | 4,25 4,25 | Services Services Services |
Flow rate (l/min) | Others | Services Services Services | Description Description Description Description | Services Services Services | Security security security security | Others | Services Services Services | Services Services Services | 24 hours 24 hours 24 |
Flow rate (l/min) | 3,66% of the total | 4,58% | Results Results Results | 6,39 € 6,39 € | 7,08 | 7,83 | 8.66% | 9,5 9,5 | 10,2 |
Water saving (%) | 54,2% | 54,2% | 54,2% | 54.8%% | 55.7%% | 56.5% | 56.7% | 56.8% | 57.3%% |
Saving shower RST
Pressure (kg/cm2) | 0.55 | 0.8% 0.8% | Evolution of evolution | More information More information | 1,9 | 2,25 2,25 | 2,7 | 3,1 | 3,55 |
Flow rate (l/min) | Others | Services Services Services | Description Description Description Description | Services Services Services | Security security security security | Others | Services Services Services | Services Services Services | 24 hours 24 hours 24 |
Flow rate (l/min) | Services Services Services | 6,08 | 7,08 | 8,25 8,25 | 9,41 9,41 9,90 | 10,3 3 10,3 | Results Results Results | 11,8 | 12,8 |
Water saving (%) | 37.5% 37.5% | 39.2% | 41% 41% | 41,1% | 41.2% 41.2% | 42.6% 42.6% | 45% 45% | 46.2% | 46.5% |
An example of economic savings (annual and per person)
Shower room Shower room Shower room | Sink and sink | Drainage of the cistern | Total Total | |
Daily use per person | 5 minutes 5 minutes | 3 minutes (1) | 6 times 6 times 6 times | |
Water consumption | 16 liters/minute | 8 liters/minute | 10 liters per discharge | |
Daily consumption | 80 liters | 24 liters | 60 liters 60 liters | 164 litres liters |
Annual consumption | 29,2 m 3 | 8,76 m 3 3 m 3 | 21,9 m 3 | 59,86 m 3 3 |
Energy to heat water (2) | 876 kWh | 262,8 kWh | 0 kWh 0 kWh | 1138,8 kWh |
Cost of water (3) | 1.898 ptas. | 569 ptas. | 1,424 sts. | 3,891 sts. |
Energy cost (3) | 14.892 sts. | 4.468 sts. | 0 ptas. | 19.360 ptas. |
Cost water and energy | 16.790 ptas. | 5.037 pesetas. | 1,424 sts. | 23.251 sts. |
Saving water and energy (4, 5) | 782 + 6.135 = 6.917 ptas. | 308 + 2.422 = 2.730 ptas. | 712 ptas. | 10.359 sts. |
(1) The most common uses are coal in sink (with hot water) and hand and teeth washing in basin (with cold water). To avoid complicating the calculation too much, it has been considered that everything is done with hot water, but assigned a little less than what would correspond to the sum of sink and sink.
(2) Heating of 1 m 3 of water to the shower temperature (50-60ºC) requires approximately 30 kWh of electrical energy.
(3) Assuming that electric energy is used to heat water. If gas (butane or natural gas) is used, the cost of hot water is lower. 1 m 3 water cost (including VAT) (there are great differences between municipality and municipality, for example the cost of Donostia has been taken): 65 ptas. 1 kWh electricity cost (including VAT): 17 ptas.
(4) Shower savings are 41.2% (corresponding to a flow of 16 liters per minute). The saving of faucet is 54.2% (a flow rate of 8 liters per minute). The savings of the toilet tank is around 50%.
(5) Bear in mind that the cost is per person. Therefore, if you want to calculate housing savings, you must multiply by the number of people who use these water facilities.
* guidance.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian