Manuel Martín Lomas: "It gives me a little fear to have a great hope in the short term"

bioBASK 2010 is a strategy for the development of a new business sector related to biosciences, while at the same time it is a commitment to position the ACBC in a field of low presence. The aim of this strategy is to promote the biotechnology and life sciences sector in the ACBC, based on knowledge and innovation.
CIC bioma GUNE is another step in the bioBASK 2010 strategy, aimed at promoting biosciences and the biotechnology sector in the Basque Country.
CIC bisisGUNE, like CIC bioGUNE, is a center created to carry out high-quality, basic research. The aim of this centre is to generate, produce, promote and, of course, apply scientific and technological knowledge in biomaterials.
Biomaterials are biologically functionalized materials to fulfill a certain function in the organism. The biomaterials sector is very broad and has been extending year after year. Biomaterials can be bioactive or biodegradable polymers, such as implants in dentistry or surgery. This is, in short, of biocompatible materials or used in the field of life sciences in general.
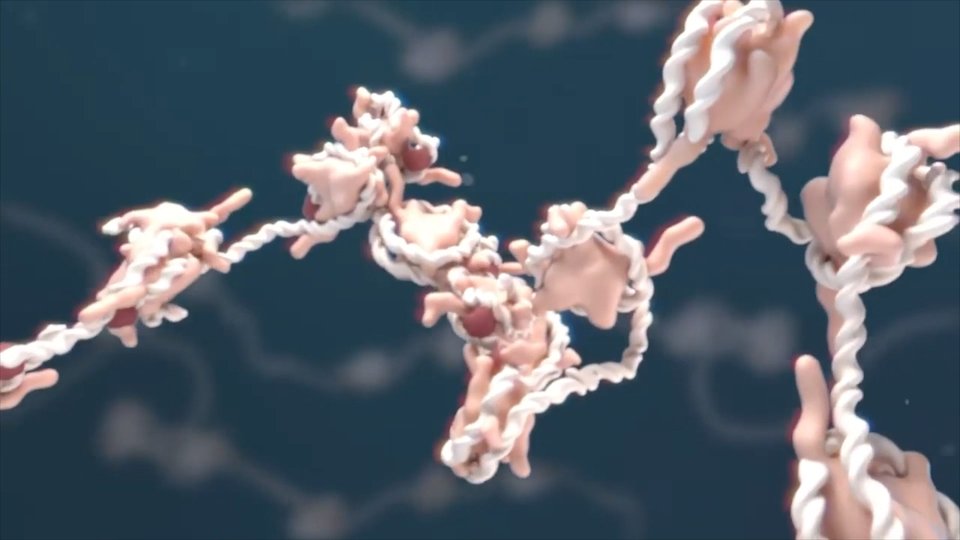
The main research lines working in the center can be summarized in three key words: biomaterial, bionanocyte and biotechnology. In this sense, the main research lines of the laboratories focus on the study of biofunctional nanomaterials and biosurfaces.
Biofuntional nanomaterials are materials of nanometric dimensions oriented to the fulfillment of a certain biological function. In the case of biosurfaces this functionalization is carried out on a structured nanometric surface. That is, in some way, the difference between the two. The preparation of biosurfaces can be done in various ways and its realization is important in some aspects of the biomaterials used in society. For example, how does a living cell react with an inorganic material? The case of titanium, used in implants, is an example.
On the other hand, biofuntional nanomaterials can be biosurfaces.
Professor Soledad Penadés' laboratory has been investigating the phenomena of molecular study for several years. That is, to investigate how a biological molecule knows another biological molecule in the physiological medium. This interaction generates a response. It seems that this adhesion or interaction between cells occurs, to a large extent, among the carbohydrates present on the outside of the cell. During the investigation of this interaction or adhesion, different biomaterials were prepared. These biomaterials are able to replace this external structure of the cell. It is curious, but we started working on biomaterial.
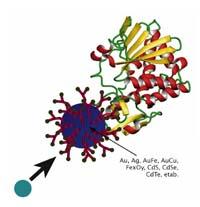
We currently have an important AIDS project in the Gliconanotechnology laboratory of CIC bioma GUNE, directed by professor Soledad Penadés. In the laboratory, we prepare nanostructures with different structural motifs of a protein that collects the AIDS virus. The AIDS virus is surrounded by gp-120. The structure of this glycoprotein consists of several carbohydrates on the outside. There are more than twenty-four structural reasons. This is one of the problems that the AIDS virus has. Therefore, we work on the development of gold nanoparticles with various motifs of the gp-120. More than one may ask: and why the gold? Its preparation is very simple and has adequate properties. This nanomaterial replaces the outer cover of the AIDS virus and can be used to prevent virus entry into the cell.
Another line of research in this unit focuses on the preparation, characterization and applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Biofuntional magnetic nanoparticles can be prepared in various ways and have interesting applications such as contrast or biosensor. Interestingly, the gold nanoparticles of less than two nanometers operated with carbohydrates present their own magnetism at room temperature. We investigate the origin and consequences of all this.
We have underway several projects on biosurfaces, but still could not speak much of them or their results. Experts are studying different aspects of biosurfaces and preparing them differently. Some work with lipids, both in metal and silicon surfaces or microns. They try to identify biological membranes and understand their aspects.
To study the properties and applications of these surfaces, the use of the atomic force microscope is important. It is a very powerful tool that allows to visualize the molecule almost entirely in biological samples. For example, it helps to see where a protein is located, how it is united, how it reacts...

Perhaps within a year we can talk more about the development and trajectory of these projects.
The new Molecular Imaging Unit will be the largest technological platform created so far, not only in the Basque Country, but also in the Spanish State.
In this unit we intend to develop products and techniques capable of observing the biological phenomena of living animals at cellular and preferably molecular level.
For this purpose, the CIC bioma GUNE Molecular Imaging Unit is structured into three main axes: magnetic resonance imaging, tomography and cyclotron or radiochemistry section.
As for magnetic resonance imaging, the development of new contrasts will be an important issue. The contrast is, in short, something that is used to make the inside look. Therefore, before doing an MRI, they make us take a contrast, for example.

In the case of PET tomography and{, radioactive products are used as a contrast. Therefore, the latter is closely related to the radiochemistry section. In fact, to carry out this type of research, it is essential to prepare radioactive isotopes in the cyclotron. These radioactive isotopes, once incorporated into the corresponding molecule, are injected into animals for experiments.
It seems that this scientific policy has aroused a great interest in the Basque Government, and that, for example, is very exemplary for me. However, it gives me a bit of fear to have a great short-term hope. In general, a research center needs 10 years to consolidate itself. I try to give this message whenever I can.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian