Need for controls
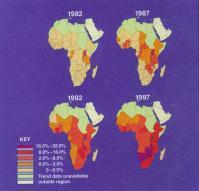
Around the world there are 33 million people affected by the AIDS virus. 70% are in Africa. It is a scary fact. Developed countries have stabilized pollution. In Africa, however, pollution continues to increase. Something must be done.
AIDS research also has very different starting points between countries. Europe and America try to unravel the relationship between the virus and the immune system. In Africa no. Their main need is to stop pollution. And they are working on it. But for this it is necessary to know the mechanisms of pollution.
The degree of contamination is higher in some populations than in others. To find out why, Antwerp epidemiologist Anne Buve has launched a major research to compare sexual habits. Around 1,000 men and 1,000 women have been elected by four cities. The research has been conducted in Beningo Cotonou, Yaounde Cameroon, Kisumu of Kenya and Ndola of Zambia. In the last two it is observed that the degree of diffusion is much greater.
Unexpected results
Researchers have not found a clear relationship between the spread of AIDS and the four expected characteristics. These four characteristics are the number of lovers, the relationship with paid sex, the use of condoms in those relationships and the age of the first sexual relationship. "We believe that the very effectiveness of disease pollution has more influence than sexual habits," says epidemiologist Anne Buve.
For example, cities with the greatest spread of AIDS are those with the lowest number of male circumcisions and those with the highest number of ulcerative diseases. Confirmation of these results will lead to the reorganization of prevention campaigns. The trend of current campaigns will be directed towards habits, but we will have to keep track of ulcerative diseases, the distribution of condoms and perhaps the promotion of male circumcision.
Another remarkable feature of AIDS research is that progress in developed countries is not easy to bring to Africa. For example, it is known that the famous drug TR can prevent contamination of unborn children. In 1997, 500 such contaminations occurred in the United States. In that year there were 600,000 cases, 90% in Africa.
Several studies have found that breastfeeding can spread AIDS. But the other options don't have to be better. Due to water pollution in many places, steppe diseases have made infant mortality a huge mortality.
Research with prostitutes has also yielded unexpected results. 15% of the collective analyzed were uncontaminated women, although they have maintained unprotected relationships with contaminated clients. Some abandoned work for two months and became infected in the following contacts. The explanation may be that a daily contact is needed to have a certain immune barrier. If this is true and an AIDS vaccine is obtained, it may have an effect if it is only taken continuously. It is a complex issue.
AIDS is affecting Africa in recent years. But research is spreading. Next summer 10,000 researchers will meet in Durban, Afika Sur, in the 13th edition of AIDS. world conference. This is the first time it has been done in a poor country.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian