In space, garbage everywhere
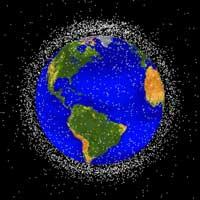
According to a calculation by the European Space Agency, we only use about 6% of the material that revolves around the Earth. The rest are satellites we no longer use, rockets sent to orbit satellites and remains thrown into spacecraft explosions.
Some particles are very small, such as paint litts, but their small size does not mean they do not cause damage. They move at high speed, traveling about six kilometers per second, making them dangerous for both other active satellites and spacecraft and astronauts. At this speed they can cause great damage when colliding with spacecraft.
Of course, the greater the particle that caused the shock, the greater the damage caused. Spacecraft carrying crew members, such as the ISS, avoid large amounts of garbage that go against them, maneuver to prevent them from colliding with garbage particles. However, small particles are not noticeable and collision with them is often inevitable. Space ferries (vehicles used in the United States to transport astronauts) often have craters caused by the collision of small particles of garbage when they return to Earth.
Clean the space

It is logical to think that the more satellites and spacecraft put into orbit, the more dangerous the orbit around Earth will be. And it is clear that astronomers will continue to send satellites and spacecraft for their research. But they do not want space around Earth to become a dangerous place for missions and all the space agencies of the world begin to work.
Some satellites have approached Earth to enter the atmosphere through gravity. In short, the closer a satellite is to the Earth, the more the gravity of the Earth will influence it and it will be easier to penetrate the atmosphere. At the time of their entry into the atmosphere, they are greatly destroyed, disintegrated due to the friction produced by the atmosphere.
Others, for their part, are too large to be destroyed once they have entered the atmosphere and have a high risk of collision with Earth. For this not to happen do the opposite with large objects: They drive them away from the earth. The truth is that the only thing they get is not to disturb the satellites running (you can not say that it is a very clean solution).

On the other hand, it is thinking of using new technologies to make satellites. The European Space Agency, for example, has begun to create very small satellites. Due to their small size, they plan to send fleets formed by many satellites to replace the large satellites that are currently underway.
The advantage of small satellites versus large satellites is that, once the work is completed, they will eliminate them by entering the atmosphere. And so, the space around the Earth will be cleaner. While it is in favor of the well-being of our astronauts and satellites, it is a very important issue.
Published in Deia
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian