Refractive defects
Myopia:
The eyeball and the tilt of the cornea are larger than normal. As a result, light rays focus on the front of the retina and distant objects are blurred. However, close vision is correct.
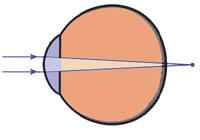
Farsightedness:
The eyeball and the tilt of the cornea are lower than normal. As a result, light rays focus on the back of the retina and nearby objects are blurred. However, remote viewing is correct.
Astigmatism:
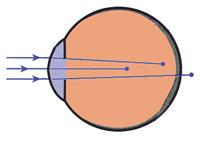
The shape of the eyeball is not spherical but elliptical, so the focus axes will be of different dimensions. The focus of light will occur at different points. Conclusion: the object may be well focused horizontally, for example, but not vertically. The result will be a blurred vision. Astigmatism can be accompanied by nearsightedness or farsightedness.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian