The adventures of the Venus Express probe on Venus
2008/03/02 Lakar Iraizoz, Oihane - Elhuyar Zientzia

Nine articles, thirty-four pages, all to talk about. The main conclusion of the natives is: Although Venus and Earth are similar, these research shows that they are more similar to what we thought. However, research will serve to understand the differences between both planets.
Venus and the Earth, the same?
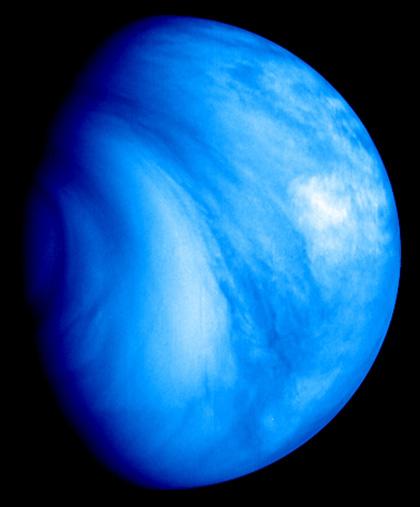
Venus is a terrible place for us. Its atmosphere is compact, formed by carbon dioxide (think about its greenhouse effect), has clouds of sulfuric acid at almost 500 degrees. The atmospheric pressure on the surface of Venus is 90 times higher than that of the Earth and the corrosion is enormous. In October 1975 a probe landed on Venus and lasted less than an hour.
The Venus Express probe is externally investigating the atmosphere of Venus. Thanks to this, scientists have demonstrated for the first time that rays are produced and that oxygen and hydrogen are poured out of the atmosphere into space together with helium. That is, they have seen that the planet loses water components. No wonder you are dry!

On the other hand, scientists have been surprised by the existence of a hot layer in the supposedly cold part of the atmosphere. So far he was called cryosphere... now they may have to change their name.
And how does this terrible planet resemble Earth? The size, mass and density of Venus are similar to those of Earth. We already knew that. But data from the Venus Express mission also indicate two atmospheric swirls, the north pole and the south pole. And there comes the similarity. They are similar to the atmosphere over Antarctica... of the part of the atmosphere that has the hole of the ozone layer.
Technical problems to solve to arrive
Astronomers want to study the planets of the solar system to better understand the changes taking place on Earth. They say that it is not enough to look at the atmosphere of our planet, but also to look at others and analyze their behavior. The atmospheres of Mars and the satellite Titan of Saturn have already been analyzed.
On Venus they especially seek the answer to a question: How is it possible that two planets of such similar size, mass and composition have evolved so differently over the last four million years?
The probe they have built for the Venus Express mission is based on the Mars Express probe, which was sent before to study Mars. However, they could not do the same, as each probe faced specific conditions.

The solar panels of the Mars Express probe were shredded and fitted the surface to, among other things, produce the Venus Express. (Photo: ESA)
The condition that most influenced was the distance of the planet to study with respect to the Sun. Mars is farther from the Sun than the Earth, while Venus is closer (28% closer). Important adaptations were made in the Mars Express probe to address this difference.
On the one hand, the entire surface of the probe was conditioned to cope with higher temperatures and, on the other, the solar panels that supply energy to the probe were conditioned. As the Venus Express was approaching the Sun, they saw that it was going to receive much more energy than the one that traveled to Mars. Thus, solar panels that supply energy to the probe were much smaller.
All necessary adaptations were made in the probe and the Venus Express mission was launched. Its route will be around four years and is scheduled to end in mid-May 2009. To see what news brings us until then!
Published in 7K.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia