Kissing disease, more frequent than expected
2004/06/01 Agirre, Jabier - Medikua eta OEEko kidea Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
It mainly affects adolescents and young adults, especially in developed countries, but in developing countries there are many cases also among children. In children the process begins and ends with hardly any symptoms, which gives immunity to the child so that he does not contract the infection again.

Mononucleosis is not contagious and affects less than 15% of the most exposed. In fact, university students are most affected by their age and habits.
Transmission and symptoms
Man is the only source of infection of this virus. It is transmitted mainly through saliva, so it is called “kissing disease”, since the most common way of transmission is to kiss in the mouth. This explains, on the other hand, that the disease manifests itself among young people of both sexes (15 to 25 years old) and that it is more rare in young adults around 35 years old.
Most infections that occur in infants and children do not have symptoms and cause at most mild pharyngitis with tonsillitis or without angina inflammation. In the case of adolescents, 80% have a typical symptomatology of mononucleosis. When jumping older people, uncertain symptoms appear: fever for a long time, discomfort and muscle pain.
Epstein-Bar virus (EBB) belongs to the herpes virus family and once infected a person adheres to B lymphocytes, in which immune processes are created and altered.
After a long incubation period (between 30 and 50 days in adults and young people, between 10 and 14 days in children) there appear a series of symptoms typical of other processes such as headache, fever, fatigue... But within a few days there is a trio that characterises the disease: fever, inflammation of the pharynx and tonsils and adenopathies (semi-consciousnesses).
Fever occurs in all cases of mononucleosis, is high (39-40ºC) and occurs mostly in the afternoon. It can last more than a week.
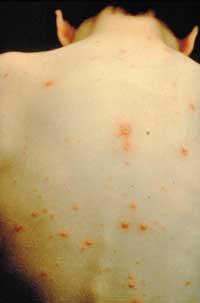
Inflammation of the throat appears in 85% of patients and covers the entire throat. Half of the patients leak fairly ugly with debt. Semi-concise (adenopathies) are lymph nodes that increase, especially in the neck and behind the ears, but in some cases inflammation or inflammation of the nodes can spread not only to the neck, but also to other parts of the body. Pain when touching the seedlings. Adenopathy takes 3-4 weeks to go away.
In some cases, inflammation of the throat can cause a blockage of the upper airway to require special attention. Other signs or symptoms do not always appear: tiredness, increased spleen size (splenomegaly), even liver (hepatomegaly), increased eyelids (edema) and an exanthema of the entire body.
What is the most appropriate treatment?

Infectious mononucleosis has no specific but symptomatic treatment: bed rest during fever and pain relievers or antithermic pain and fever
The only cause for antibiotic administration is for the doctor to consider that an additional infection (called overinfection) has been added, although they are usually not used broad-spectrum (such as amoxicillin or ampicillin).
In any case, treatment will always be prescribed by the doctor and in no case by the patient.
Antibiotics (aciklobir, etc.) have not been as adequate as expected. Polishing procedures of the garga as a result of an uncomfortable inflammation of the throat can be beneficial. And when complications appear (V. Table) there is no choice but to use corticosteroids.
Research to create some type of vaccine is underway, but prevention is the only way. How? Since humans are the only source of the virus and the infection is transmitted through saliva, if infected, kisses should be avoided. But as in the beginning it goes unnoticed, unfortunately the diagnosis of the infection is made when the symptomatology is very clear and by then it is possible that the infected person contaminates another person.
Mononucleosis heals within a maximum of two months if no complications occur. The disease is benign and usually after 3-4 weeks the patient is quite recovered, although fatigue and increased nodes no longer disappear.
Complications
- Complications. They are rare: meningitis, encephalitis, facial paralysis, etc.
- Rupture of the spleen. Rare (0.1% of cases) but severe complication. It can occur from small or spontaneous trauma.
- Liver disorders. They are more frequent but not a serious problem.
- Anemia, usually hemolytic, from broken red blood cells (2% of cases). Sometimes platelets also decrease.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia