A long way to go
2000/04/08 Roa Zubia, Guillermo - Elhuyar Zientzia
Celera lacks a lot of work to read the full code of the human genome.
Celera Genetics announces that the decoding of the human genome is about to end. However, he lacks a lot of work to do. Despite reading almost all the information, they are still disordered fragments. Therefore, the structures and functions of proteins are not yet known.
The processes that our body must perform are made by proteins. They destroy food, transport oxygen from the breath, give color to the eyes, avoid diseases as much as possible and fulfill thousands of functions. We have, therefore, many different proteins working in the body. But, how does the body know how each protein is? This information is in the genome.
This information is encoded. A gene is a protein information code. About forty years ago the biochemists learned to decipher the code and from there they began to read the code of the man. The code has a simple structure. DNA is stored in special subunits that can be read ordered in long molecules, as if they were letters. In addition, the four possible repeat subunits are represented with the letters A, T, G and C. These three subunits encode a part of the protein. We read the following three and will know what the next part of the protein is. And so you can continue to form the protein. The part of DNA that encodes a protein is called gene.
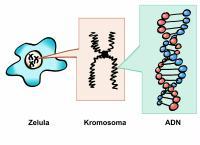
Of course, the information we need for human beings is enormous, because we have a very complicated organism. As we have many genes, our genetic information needs a precise organization. Genes are joined together in large structures called chromosomes. However, because it is a lot of information, not all genes can be united on a single chromosome. That's why we have 23 different chromosomes. For other reasons, however, this information is duplicated. Thus, at the core of each body cell there are 23 pairs of chromosomes. Decoding the entire genome will allow you to know what each protein does. Nor can one perceive half of what can come behind.
Access to all this information is a heavy work because you have to read all DNA. There are many strategies to carry out this work. The choice of Celera Genomics is based on the rupture of the DNA molecule. The readings are about to finish, but to start doing something you have to sort the code and correctly place the pieces of each protein.
Despite this, the employees of Celera Genomics will have a laborious job. Then they will have to clarify the function of proteins. In addition, many times to fulfill a single function a group of proteins is necessary, that is, to know what are the proteins that work together. The genome project has a long way ahead.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia