Aging process, desire to return to youth
2000/05/21 Kortabarria Olabarria, Beñardo - Elhuyar Zientzia
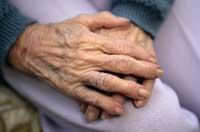
Eating habits and human eating are getting better and healthier. The advances of recent years have made what medicine can do for the benefit of human beings more and better. All this has allowed the life expectancy of human beings to grow more and more. However, human beings have not been able to influence the aging process. We earn more years, but aging is not interrupted. In this way, many of the faculties that characterize youth slowly disappear, the movements of people slow down, the ability to control movements is lost... until other questions are asked in the brain: Wouldn't it be better to finish as soon as possible? Is it worth living like that?…
Logically, as a result of the above factors, the aging process itself is currently better than a few years ago, and many diseases that were once unsustainable are easily resolved. Science, perhaps with the use of "artificial" resources, has managed to extend people's life expectancy. It is not little, but the goal of science goes further. In order to be able to pass healthy these last years of life, science aims to slow down the speed of aging of people. To do this you have to understand well what aging is and what aging means.
It seems that science comes everywhere, has an answer for all questions or at least can have a very close answer, but there is still no answer about the aging process. Scientists don't know why beings age, why they age to death, and why some age faster than others.

In general, biologists consider the body as a machine, a set of organs and tissues properly coordinated. As time passes, this machine would "spend" itself and in that process the environment would also be affected. However, the aging process of the body, not even as a machine, is not entirely homogeneous. For the organs and tissues that make up the body, time does not pass the same, each of these components can withstand the passage of time in many ways. When a basic component commits an unsolved vacuum, when it exceeds the limit, it can cause death, even if the state of the other components is good.
Despite its almost total autonomy, in old age different processes are developed simultaneously and in the same direction. Therefore, we should mention some indicators of old age: hearing loss and vision, loss of muscle and bone mass, increase of fat, loss of brain mass, loss of flexibility, etc. and in turn, increased risk of contracting certain diseases.
The causes of aging are unknown, but some clues can be found. The body can be considered a set of hyperspecialized cells. These cells are constantly fed and divided. Copies of genetic material are made during cell division. This process is complex and errors or mutations can occur in it, by chance or by external influences such as radiation. The older the body, the greater the possibility that some mutation may influence the proper functioning of the cells. Many types of cancer, for example, remain hidden for years until their onset in old age. According to experts, mammalian cell genes can be damaged every day 73,000 times. If they did not have enzymes for repair, the cells would die soon.

Metabolism also affects cells. In order to grow and divide, cells need energy and organic matter. For this, humans need oxygen, but this element can be dangerous to life. Oxidation can cause genetic damage to cell division and must be repaired by the cell itself. However, sometimes the passage of time causes the cell to lose the ability to repair defects, so mutations can cause problems that can not be overcome later. The life of beings with a very fast metabolism -insects, microorganisms, colibrias, mice...- is usually short, while those with a slower metabolism, such as man or turtle, are longer. Beings with fast metabolism first have old age and die before. Therefore, it is said that a diet with fewer calories than usual, with adequate nutrients, can extend life, since the metabolism does not affect the cells so much.
It seems that the limit of human life expectancy may be around 115 years, but reaching those years is not easy. In the Middle Ages life expectancy was 25/30 years and people 50 years old were very old, today - in advanced territories - is higher. But both in the Middle Ages and today, reaching the border was not common.
Human body cells are not able to divide permanently and forever, at least if they are not cancer cells. At the ends of the cell chromosomes is a fragment called a telomere. Each time the cell divides, the telomere is slightly shortened. It seems that the telomere can be divided a maximum of 50 times, no more. Cancer cells, on the other hand, contain an enzyme called telomerase, which has the function of replacing the telomere and that the cell division is continuous. When the cell cannot be divided, unrenewed tissue ages and dies.
Other factors that can influence the cellular aging process are: damage to essential proteins, accumulation of toxins, immune problems, etc. One knows whether they are a consequence of the aging process or whether the aging process is a consequence of these factors. There is a clear thing, on the path of research, perhaps of the formation of the human genome?, the causes of the aging process can be known, but it can hardly be affected. It would not be natural -good.
Published in 7

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia