MagellMagellan
1991/07/01 Arregi Bengoa, Jesus Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
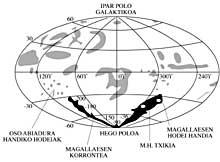
Analyzing the interaction between clouds and our galaxy in Magellan, we said there were also reasons to talk about these clouds especially. It is time to mention the particularities of these satellites of the French Way.

In the dark nights you can see very well at first glance in the sky of the southern hemisphere. Therefore, they are cited in the mythologies of the inhabitants of Australia, the Bushmen of South Africa and some cultures of the Pacific islands. His name, however, is due to the Portuguese sailor Magallaes, who described him accurately in the chronicles of his trip around the World in 1521. As most irregular galaxies are small.
The diameter of the largest (Large Magallanic Cloud, LMCP) is about 20,000 light years, that is, the fifth part of the French Way, and the SMS (Small Magallanic Cloud) of about 10,000 light years. As for the mass, CML is 10,000 times that of the Sun and SMS does not exceed 20% of the rest. The mass calculation was performed by analyzing the turn curve. In the case of the FRM, for example, the maximum rotation speed of the stars is only 70 km/s, while that of the Sun (around the center of the French Way) is 250 km/s (in general, in the spiral galaxies the speed is 200 km/s and 300 km/s.
As for distances, the Great Cloud is about 150,000 light years and the other about 200,000 light years. As you can see, this last distance is only twice the diameter of the French Way. This relative proximity facilitates the separation of stars. Precisely at the beginning of the H century. The study of the hundreds of variable primes found by Leavit has allowed us to calculate the distances mentioned. Its accuracy is 10%.
At the same distance level as the Magellan clouds, there are two other galaxies smaller than them: Draco and Ursa Maior systems. It is believed that all these galaxies could be traversed around 2 billion years.
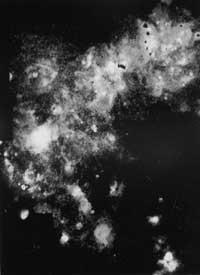
In addition to variable primes, other types of stars such as red supergiants, OB spectral types, RR Lyrae variables, Wolf Rayet stars (very hot and bright stars that have lost their surface layers), etc. can be distinguished. Also interesting are star clusters, but highlights 30 Doradus (NGC 2070) of the LMCG. It is a HII region, that is, a huge cloud of ionized hydrogen, heated and ionized by the stars that have formed inside. Its diameter is 1,500 light years, one of the largest known star clusters. It does not have a specific location within the Great Cloud, but is usually considered the nucleus of the galaxy.
30 In the center of Doradus there is a very bright mass. It is called R136 and has a width of about eighty light years. It is not clear how it is, but it is believed that in part it can be a weak version of the processes that occur in the cuases. Therefore, the study is very interesting. Moreover, in February 1987, in 30 Doradus the supernova A was created, making this cluster of stars even more known and interesting.

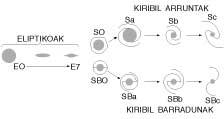
The Big Cloud, structurally, has a long light bar inside a thin disc, but the turning center is not inside the bar, but a little further north. This means that the bar only has a small part of the mass of the galaxy. Around the bar you can see the star clusters, but without a defined structure. Among irregular galaxies there are others of the same appearance. All of them are those we classify in the Irr I group of irregular galaxies. The light bar also appears in SMC, but with a particularity. At one end it has an esplanade that gives it a pear shape. Unfortunately, we see this structure in a transversal way and it is difficult to give more details.
Another detail to consider is the high percentage of gases contained in these galaxies. 10% of LMCC is gas and 20% SMS. At the same time, the percentage of heavy elements (carbon, oxygen,...) is lower than in spiral galaxies. These two particularities indicate that the evolution of the Magellan clouds has been slower than ours. The process of star formation and the enrichment of interstellar matter are slower. The reasons for this slowness are not yet known.
As is known, the Magellanic Clouds are located at one end of the Magellanic Current and also surrounded by a giant hydrogen cloud. Some astronomers prefer the Magellanic Clouds to be considered the core of this cloud. On the other hand, according to the neutral hydrogen distribution studies conducted by radiotelescope, the SMC appears to be made up of two opposing clouds. The older of the two would be 20,000 light years closer to us. Perhaps these sections are the result of a recent clash between the two Magellanic Clouds, with the SMC broken by impact.
EPHEMERISSUN : August 23 enters Virgo at 15h 12min.
PLANETS
|

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia