Homo floresiensis, new human species on the island of lost hominids
2004/11/02 Orruño Aguado, Estibalitz - Elhuyar Zientziaren Komunikazioa
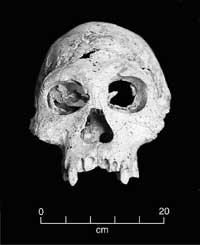
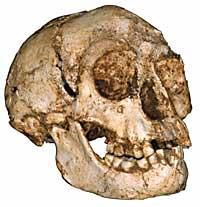
The remains have been found in the cave of Liang Bua. The journal Nature has published that the skull of a mature woman and several bones have been found along with fragments of the skeletons of six other individuals. It seems that the remains of hominids were not fossilized and have had to handle the bones very carefully. In addition, in the same place they have found tools of stone and bones of the Komodo dragons and a tiny elephant known as Stegodon.
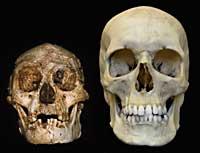
The skeletons found have been classified within the genus Homo and the new species has been called Homo floresiensis. Liang Bua's hominid skeleton presents great differences with that of Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. However, according to archaeologists, the hominid of Flowers was the successor of H. erectus, Asia. Our species, H. sapiens, also comes from H. erectus, Africa. However, the DNA of the new species remains to be studied. Once the results of this study are known, scientists will be able to perform a definitive classification.
Using two different dating techniques, the traces of H. floresiensis have concluded that they are about 18,000 years old. Therefore, at this time it is possible that our species and H. floresiensis live on this Indonesian island. It is really exciting to know that the hominid so different from us lived little time. H. sapiens has not been the only species of hominid on our planet until very recently. It is still impossible to know the interaction between these two hominid species. Perhaps H. sapiens killed the little hominids? Or did H. floresiensis disappear because it could not compete against a species larger than it to obtain food?
Reduced by insulation
Insular isolation has led to the emergence of endemic nanisms in some mammals. It seems that the island conditions make some animals smaller than normal. Among them, limited island resources and greater protection against predators are the main agents. In short, nanism is the result of a process of adaptation. Some animals of the islands have observed spectacular cases of nanism. One of the most striking examples is the dwarf elephant of Sicily and Malta. In these cases, from forests of four meters of length, they became elephants of little meter in a short term of 5,000 years. They believe that the hominid discovered in Flores can also be the result of a process of nanism of these characteristics.
Child, monkey, pigmeo... What will it be?
The skull of H. floresiensis has a volume of 380 cubic centimeters. Approximately one-fourth of the current human population. Therefore, when archaeologists discovered the hominid they believed it was the skeleton of a child. However, when the wear of the teeth was detected, they soon realized that these remains were the most mature hominid.
Because of this small size of skulls it could also be thought that it could be a monkey. However, the morphology of the skeletons of Flores does not coincide with that of the monkeys. Among other things, the new species has small canines and must be obligatory of two legs. For these characteristics it has been classified within the family of the hominids.
If you are not a child or a monkey, is it possible that the findings of Australopithecus are in Indonesia? The answer is once again negative. Because the body parts of H. floresiensis and Australopithecus have different characteristics.

A fourth chance occurred to some. That the traces could belong to a H. sapiens pigmeo. In general, pygmy men are quite small, between 1.4 and 1.5 meters in length. However, the size of the head of the pygmies is not much smaller than that of normal men. Therefore, the hypothesis of the pygmies is also annulled.
Was the new hominid capable of using tools?
The hominid of Flores has become a source of discussion on whether he was able to use tools. As mentioned above, in the same place of the remains of H. floresiensis, stone tools have also been found. Archaeologists who have discovered it claim that the hominid of Indonesia used these instruments. However, other scientists have denied the above. According to the latter, the utensils found in the site do not belong to the same time as the skeletons. Thus, it is possible that these stone tools are of H. sapiens.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia