Parasites of childhood
1989/02/01 Agirre, Jabier - Medikua eta OEEko kidea Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
Under this main title it is intended to gather a wide variety of situations, but highlighting common characteristics for all. And what are those common characteristics?
- These diseases, although they may appear at any age of life, have special characteristics in childhood and especially in school, especially when it comes to pollution.
- The causes of these diseases are parasites, h.d., living things that live from the back of another (in these cases of the girl). They are usually quite large and visible to the naked eye.
Lice lice lice eyes
It can be thought that lice were something ancient, something that had disappeared for today's society. Unfortunately, for several years these parasites have increased considerably. These reproductions coinciding with some stages or stages of the school year, since children are very frequently infested with these insects and sources of contamination are very frequent places.
It cannot be thought that nowadays lice are something exclusive of territories with a low socioeconomic status, since they are extended to all social levels. And therefore, they should not be reasons of complexity or generate feelings of guilt. But it must be accepted as a human problem.
Types of parasites
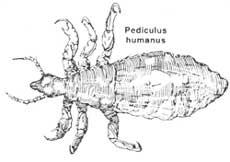
Lice can be of three species:
- Head lice (Pediculus humanus var. capitis)
- Piojo corporal (Pediculus humanus var. corporis)
- The chance of the testicles (Phthirus pubis)
Life cycle
They have sexual dimorphism: normally male lice are smaller than females.
When the eggs are laid, these eggs (BROWN), of 0.6 to 0.8 millimeters, are accreted in the roots of the hairs by means of a mass or insoluble paste in water, so they are separated mechanically. The eggs are laid at night in the root of the hair about 2 cm from the skin. Each egg is subjected to a hair.
The development of the egg totally depends on the outside temperature. At 35-37ºC the larvae leave 5-7 days later. As the temperature drops, the larvae need more days to develop (8-10 days at 25-30ºC and 16 days at 22-24ºC) and below 22ºC the development is interrupted. If this cooling lasts more than seven days, the egg is not able to carry out the development cycle.
The larva, after 2 weeks after having suffered 3 changes, has matured sexually and after a blood shot, is ready to start producing eggs. The average lice have a life cycle of 20 days, depending on the temperature.
The adult pommel is lived in a month. This theoretical life is summarized a little, since mortality is high (by deposition, hairstyle, etc. ). The aged, sick, or dead lice fall from the head.
It has been calculated that the head lice lay about 150 eggs throughout their lifetime. Piojo is a persistent parasite. In suitable conditions (suitable for lice, of course! ), 60% of spawned eggs can become ripe.
Transmission, information (pollution)
The lice are placed on the head (and especially between the hairs). The hair is altered, dried and can fall, especially in women, where chance finds very favorable conditions (especially long hair).
Lice suck blood for long periods. They can live between 15 and 38ºC, but die above 40ºC. The wet heat disappears the eggs at 60ºC for 15-30 minutes.
Head lice easily pass from one host to another and without food (h.d. without blood) are able to stay ten days. Pollution sources are, first of all, the places where a massive coincidence of people occurs (schools, kindergartens, camps, etc.) Special attention deserve schools and nurseries, which in their games can easily spread to children. The exchange of hats or similar, the common use of combs and toys, etc., represent a quick extension of the head lice.
By age, women are more numerous than men (at any age). But above all, they are children, and at any time, those who are most aggressive during adolescence.
The transmission is mainly produced by DIRECT RELATIONS. Combs, red, etc. Common use also facilitates pollution. Lice that fall from the head are always dead or injured and therefore have no risk of information.
Why are lice so annoying? Because they suck the blood often and when these bites are repeated over and over again they produce a great itching. The most vulnerable place is the contour of the ear; the back of the head, the leometer.
Each person has different sensitivity: when making the finger increases inflammation (and infection by the subsequent bacteria). This and the spice of lice can form scabs, chickens, and foxes. In case of attack of the eyelashes, conjunctivitis may also appear.
Prevention of prevention and prevention
The first sign of lice can be itching (increasing) and deposition. It is important to locate the source of contamination as soon as possible to prevent more infestations from occurring.
In preventive matters, the following points must be met:
- Frequent hair wash with normal shampoo (2-3 times per week).
- Comb well the hair daily, cleaning well these useful.
- Check the children's head well, once or twice a week, watching the plots, especially in the back ears and in the neck.
The distance of the plots to the skin will indicate the age (or number of days) of the infestation.
It is also convenient to study other family members.
Treatment should only be done when parasites are seen.
Treatment of treatment Treatment
First, there are two types of drugs in trade: lotions and shampoos. The lotions remain longer in contact with the hair, their level of penetration in the eggs is higher and therefore have greater ability to undo the eggs. If shampoos are cleared and, despite destroying adult parasites, they have much less influence on eggs.
- Pyretrins (natural, synthetic). Strong effect on insects and low toxicity for the human being.
- Malathion, cabaryl (they are lotions). Despite violent action (against lice and eggs) its toxicity is also high.
- Lindano, DDT. Due to its high toxicity and its enormous use in recent years, resistant slag began to appear. The effect on eggs is moderate. Therefore, they are not very useful.
How to perform an adequate treatment?
- The hair should not be cleaned before giving lotion, since the hair fat facilitates the fixing of the active raw material.
- During the application of the lotion, we thoroughly wet the hair and skin. Rub gently but constantly, especially behind the ears and on the neck. Then cover the head (with a bath cap for example. ), keeping between 6 and 8 hours.
- Once preserved during this period, clean the hair. You can use normal shampoo or a pediculicide (lice killer).
- The coin extends throughout the head, rubbing well the most affected places. Keep the shampoo for 5 minutes before rinsing. The second application of the coin is recommended below.
- To lighten or boil the hair will be used water and vinegar (vinegar part and two waters). Vinegar disappears this cementing substance that sticks the plots to the hairs. After boiling the hair with water vinegar, it is much easier to take off the plots by freehand, which is the best way to do it.
- Do not use dryers to dry the hair. The hot air dries the hair but destroys the insecticide.
For the hairstyle a hard bristle comb (preferably metallic) will be used.
Treatment is repeated (3 times in total) days 3 and 6 to completely eliminate and destroy partial lives.
Combs, hair decorations, etc. They are immersed in an insecticide lotion for 5-10 minutes. Underwear, towels, bed sheets, etc. Cleaning in hot water.
To kill the plots, keep the temperature of 51.5°C for 5 minutes or 49.5°C for 30 minutes. Lice also die below their temperature. The wet heat is even better. Therefore, it is recommended to iron with steam (ironing).

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia