Novel of Physiology or Medicine for those who discovered the origin of gastric ulcer

J. Barry Marshall and J. Robin Warren.
Photo: www.hpylori.com.au
Precisely thanks to the work done by both, today we know that a bacterium is responsible for inflammation of the gastric wall, gastritis and even ulcer. Before finding the bacteria, doctors thought they caused inadequate life and stress. However, in 1982 Marshall and Warren demonstrated that the bacterium H elicobacter pylori is responsible for 80-90% of stomach and duodenum ulcers.
Warren began to discover the culprit of the ulcer. And it was the first to realize that in the biopsies of the patients there were some bacteria and, when there were bacteria, the mucosa of the stomach was always increased.
Marshall found these studies very interesting, which began to analyze biopsies of one hundred patients. In addition, Marshall achieved the growth of the bacteria in the laboratory and both saw that it was directly related to the ulcer. In all patients with gastritis and duodenum ulcer or stomach the bacteria were discovered. The researchers concluded that it was the cause of these diseases. They subsequently called the bacteria Helicobacter pylo.
Bacteria closely linked to man
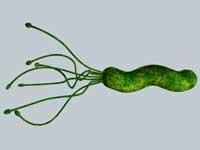
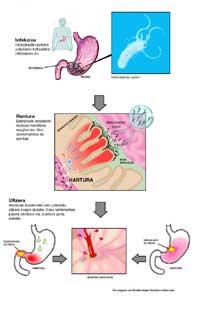
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that lives alone in the human species and is very well adapted to the stomach area. Half of the population has bacteria, less common in wealthier societies, but in developing countries almost all are infected. Normally the bacteria pass from mother to child, and although it often does not produce symptoms, 10-15% infected develop the disease.
The bacteria initially infect the lower stomach. It causes an increase in the area and it seems that chronic inflammation produces gastric acid at the top. This increases the chances of gastric and duodenal ulcers. In more severe cases, the mucosa bleeds and drills.
In addition, chronic ulcer is related to the risk of developing cancer. Although there are
currently adequate treatments for the healing of ulcers, stomach cancer is not as widespread as before, it ranks second in the list of the most lethal cancers. It
also increases the risk of developing a type of lymphoma.
Antibiotics
Warren and Marshall are responsible for making gastric and duodenal ulcers and gastritis medicinal today. Treatment is based on antibiotics and antacids with very good results. However, it is not possible to use antibiotics massively because otherwise there is a high risk of resistance. That is why they are used only to cure patients. However, what was once a chronic disease has become a remedy today.
Also, the knowledge that the origin of gastric ulcer is a bacterium has opened the way to investigate chronic diseases such as Chron's disease, rheumatoid arthritis or arteriosclerosis. Bacteria related to these diseases have not yet been found, but there are increasing indications that bacteria have a great importance in the formation of certain chronic diseases.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian