Changes in neurons during sleep are essential to create memories
2017/02/02 Galarraga Aiestaran, Ana - Elhuyar Zientzia Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria
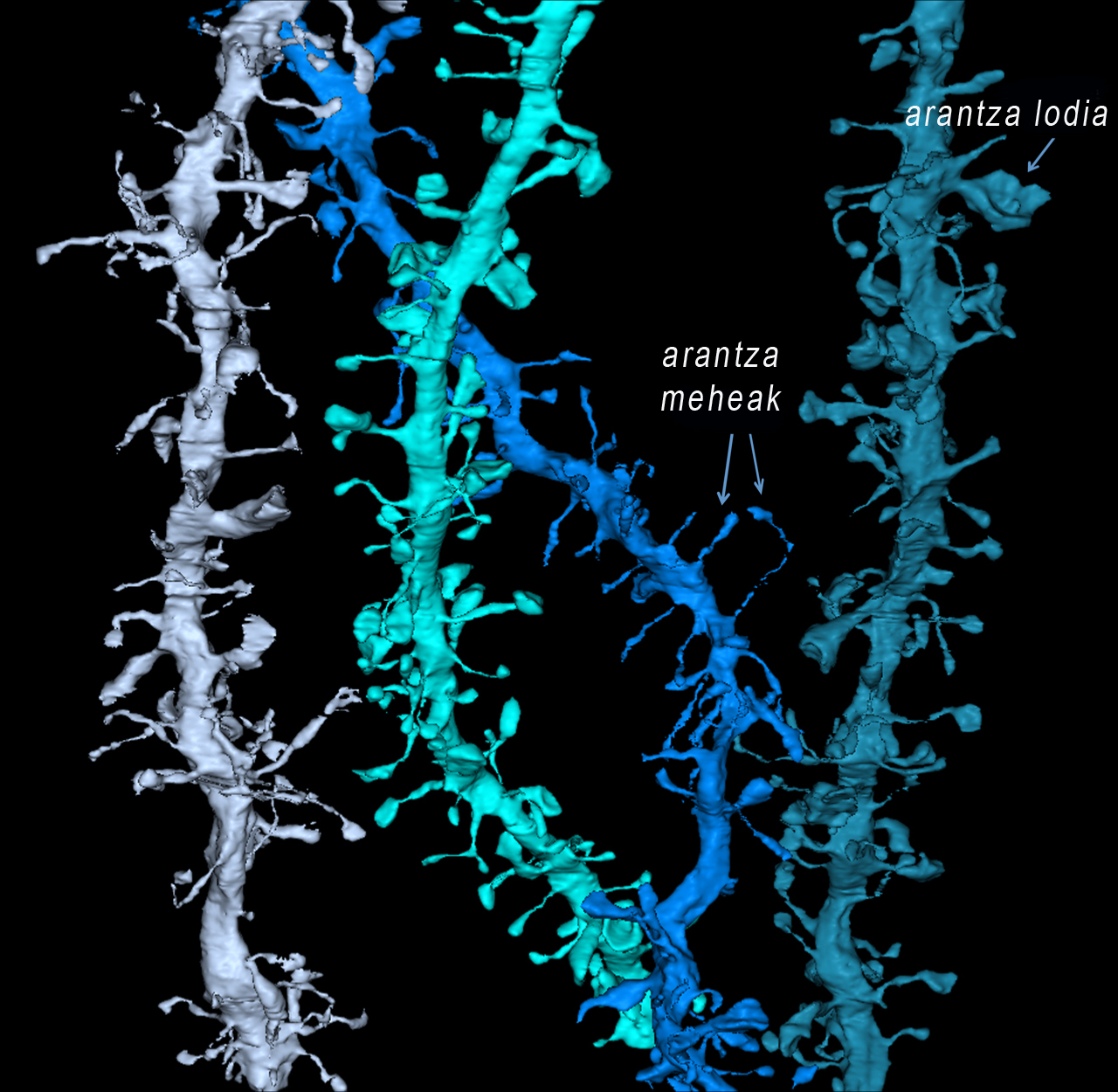
It is undeniable that sleep directly influences memory, but scientists do not know the essential mechanisms that explain it. Two studies that illustrate these processes have now been published in the journal Science. According to them, the key is the structural and composition changes that occur in the synapses: the connections that reinforce when we are awake weaken when we sleep, something essential to create and consolidate memories. Although both research has been conducted in mice, they believe the process will be similar in humans.
One of the research is led by researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Neuroscientists have studied the brain tissues of mice using electronic microscope and have created three-dimensional models of dendritic spines of neurons. After analyzing thousands of images, they have shown that synapses contract after sleeping. In particular, it has been observed that when sleeping the intermediate surface of neurons and plums decreases, while when awake the surface increases again. The researchers have come to the conclusion that with this reduction there is a correct processing and storage of information.
The second research has been conducted by Johns Hopkins University. Biochemistry, proteomics and illustration have shown that during sleep the biochemical composition of synapses and the transport of signals changes. All this weakens the synapse. In addition, the gene that guides these changes has been identified: Homer1.
Therefore, both investigations agree that the plasticity of synapses in the wake sleep cycle is the key to creating memories. In the second, it has also been related to the learning process and have shown that if these modifications are avoided in the synapses, mice do not create new memories.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia




