Evolution of the population
2002/07/01 Galarraga Aiestaran, Ana - Elhuyar Zientzia Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria

The United Nations estimates that in the last 15 years the world population has increased by more than 1 billion people. In fact, the population has never grown as much as last century; since 10,000 years ago agriculture developed, 75% of the total population growth has occurred in 1% of the time.
XX. At the beginning of the 20th century there were about 1.5 billion people around the world, in 1927 they were 2 billion, in 1960 they were 3 billion, in 1974 they were 4 billion, in 1987 they were 5 billion and in 1999 the population reached 6 billion. That is, the last century the human population multiplied by four, and in addition almost half of the world population has not yet reached 25 years.
The human population is growing at a dizzying speed, with the consequent increase in energy consumption and natural resources, which makes the environmental impact more and more pronounced. In many places, the damage caused by the human being has overcome the capacity to renew the environment and some believe that the situation is not reversible. All this has led to the growth of the population having received the attention of experts for a long time.
The last work published in May in the journal Science has raised dust. In the article, Jim Oeppen and James W. Demographic researchers Vaupel have affirmed that the life expectancy of man is extending more than expected. Not only that: in view of historical data, it has extended continuously and linearly, and in the future it does not seem that the trend will change, but it seems that life expectancy will be extended almost without limits.
The future of humanity under debate
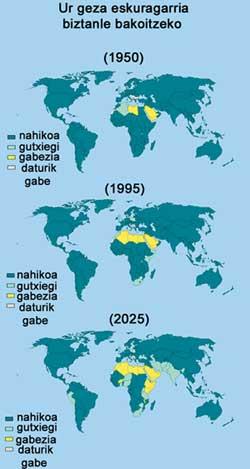
The article has received answers of all kinds and, from the most optimistic to the most pessimistic, many opinions have been published on the future of the population. In fact, demographic prediction requires taking into account a large number of factors and many times it is not known what will happen with decisive aspects. To cite only one, calculations vary greatly depending on the predictable evolution of AIDS.
It is evident, therefore, that the expectations of the experts are very different from the point of view. Broadly speaking, the liberal right-wing view is usually positive. According to them, the growth of the population is no risk. Although since the 1980s the population has grown per capita to a greater extent than agricultural land, technical advances hope to overcome this problem. Genetic engineering is an increase in land productivity, which will result in a strengthening of the rural economy. At the same time, as education reaches all women, fertility rates will decrease. In the end, they believe that the difference between rich and poor societies will disappear and believe that the Earth has an almost unlimited capacity of adaptation in climate warming. Otherwise, omnipotent science will bring about some solution.
However, taking into account the other end, science will not be able to remedy what man had mistaken. In sub-Saharan Africa, the population is expected to triple and double in South Asia, so if the situation is already bad, then it will worsen and it is expected that hunger and disaster will spread in those areas. Even worse: in addition to malnutrition, population growth will cause imbalance between countries, violence and wars, ecological disaster, lack of resources, loss of biodiversity and pollution of the environment. Natural disasters, such as floods, will also be more damaging than now, as it will force people to live in inadequate places.

Already there have been theories of solid base that foresaw the decline of humanity. For example, the XVIII. At the end of the twentieth century Thomas Robert Malthus announced that the human being was reproducing faster than food and that in the future it would have to reduce the population by means of hunger, disease, war or appropriate measures (by not using contraceptives as much as at present at that time, these measures were limited to having less marriage). Long before, II. In the twentieth century, Tertullian thought something similar, as he wondered if the plagues, hunger, wars and earthquakes would not be a remedy to limit the population and therefore beneficial to countries.
However, it is not surprising that Malthus is so concerned about the demographic explosion that occurred at that time in England. After World War II, birth also increased in Europe and then worries of this type reappeared. In fact, periodically appears the idea that the population will become extinct when it reaches a limit.
Influence of scientific advances on the population

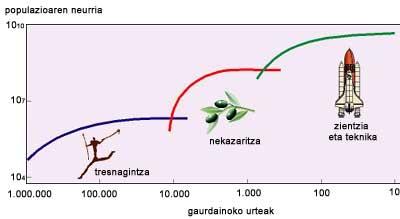
Later it has been seen that Malthus was wrong and since then other visions have been given. Among them, Edward S aroused great interest. That of scientist Deevey and his proposal is still considered. In 1960 he published in the journal Scientific American an article that explains the size of the human population from the beginning of the species. In the analysis there were three big climbs corresponding to an important technical revolution. The manufacturing capacity of the instruments, the extension of agriculture and industrial development were, respectively, the factors that led to the growth of the population. Each of them allowed access to resources that previously did not use the human being, which meant an exponential start of the population. After each growth phase, he explained that there was a stability stage.
The man began to manufacture appliances a million years ago and at that time the population went from 150,000 to 5 million. In the next 8,000 years, as hillsides and animals domesticated and developed agriculture and livestock, the population grew 100 times. At present, when only 300 years have passed since the beginning of the scientific and industrial revolution, humanity has broken the record of 600 million euros and the projection of Deevey foresees doubling or tripling the population before the growth stabilizes.

In any case, growth has never been constant; civilizations, at the highest level, have collapsed one after the other. The causes have been varied, but among them we must mention the diseases, which caused enormous killings at specific times. One of the worst was the black plague that hit all of Europe in the Middle Ages. The epidemic originated in Asia penetrated and spread through the Mediterranean ports to the north, causing the death of a third of the European population between 1346-1353, which means about 25 million inhabitants, much more than any other disease or war that existed. In another continent, America, XVI. The largest massacre occurred in the twentieth century. In fact, the diseases carried out by European colonizers caused the decline of the local population. The most pernicious were smallpox and measles, which influenced more than weapons in the conquest of America.
It grows more slowly
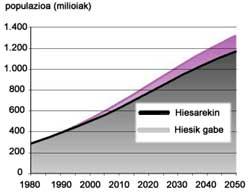
At present, advances in medicine and hygienic measures have allowed the health status of the human being to be better than ever, which has meant not only a significant increase in life expectancy, but also a significant decrease in infant mortality. Since 1950 the average life expectancy has gone from 46 to 66 years. On the other hand, as information and media are expanding, more and more women and men have the capacity to decide how many children they have. However, still about 1 billion people, one in six, live in poverty.

In developed and developing countries, the birth rate has decreased, with which the growth of the population is slowing down. China has long been implementing its one-child policy, and in developing countries in Asia, Africa and South America, since the founding of the United Nations Population Fund in 1969, the birth rate has been reduced by half, almost six to three children per woman. In 61 other countries, the number of births per woman is equal to or less than 2.1 children, so the continuity of the population is not guaranteed and a decrease in the population is expected. The United States is the only developed country in which the population grows mainly due to immigration.
However, the number of annual births has barely decreased since the peak reached a dozen years ago, when more children were born than ever, about 86 million. In fact, most of the world's population is in an ideal age to reproduce, of which more than one billion are between 15 and 24 years old. In 62 countries in Africa, Asia and South America, more than 40% of the population is under 15 years of age. Thus, 95% of the population growth occurs in developing countries, especially in sub-Saharan countries and in some areas of southern and western Asia.
In fact, the countries with the highest growth rate are also the poorest, so they cannot provide basic services or work to so many young people. For this reason, it is expected that they will go towards developed countries and that, in passing, these countries that welcome emigrants achieve their ‘rejuvenation’, since in recent years they are more and more ancient. The Basque Country is one of the oldest countries, with one of the lowest birth rates in the world and one of the longest in life. It cannot be denied that migration between countries will be decisive in social policy and in the relations of the population.
AIDS
On the other hand, it is about to see the influence of AIDS on the evolution of the population. At the moment, in Africa, above all, more people are dying than the experts initially thought: Most deaths in sub-Saharan countries are due to AIDS. We must not forget that the causes and effects of AIDS are directly related to the low level of development (poverty, malnutrition, other sexual diseases, relationship of dependence between men and women...). In many places, AIDS has overturned what it has achieved with the work of many years, both in terms of reducing infant mortality and prolonging life. For example, survival in 29 African countries is seven years younger than if there were no AIDS. In addition, some countries are suspected of hiding data and the real situation is even more serious. Faced with this situation, the United Nations has warned that if immediate measures are not taken to prevent AIDS contamination, a huge disaster can be expected, and the implementation of these measures will require international support.
Risk of resource depletion

Population growth and excessive consumption are causing the pressure that water and land resources are experiencing, day by day, to increase. At the beginning of the century, the richest fifth of the population consumes 66 times more materials and resources than the poorest fifth. As for 1950, cereal plantations per person have decreased by 50% and there are a dozen years in which cereal production has remained intact. On the other hand, the lack of water also worries: according to recent studies, by 2050 a quarter of the population will not have enough fresh water.
Unfortunately, they are not the only environmental problems, much less. The environmental groups working around the world denounce that fisheries and forests are being exploited in excess, aware of the number of animal and vegetable species that disappear in the year, and it seems that the climate is warming. While new sources of energy are discovered, humans continue to use fossil fuels and pollute the environment.
Some believe that in this century it will be necessary to make an inescapable decision: to accommodate man and his activities, that is, how many species and how many ecosystems are willing to destroy.
Human height, a reflection of well-being The welfare of society influences the individual, recognizing that the average height is directly related to food and health. Analyzing the height of the human being throughout history, it is clear that advances in food and health have not been constant, but quite the opposite: throughout history, important setbacks are observed. Robert W. The geographer Kates analyzed the male skeletons of different times, noting that height has suffered significant variations. According to data provided by Kates, the average height of hunter-gatherers living in the east of the Mediterranean between 30,000 and 9,000 years ago was 178 cm. Between 5,000 and 3,000 years ago, the first peasants of the same place only measured 160 cm. Its food was based on cereals and the agricultural work was hard and laborious, but over time the situation improved and the technique was developed. This allowed farmers from 1.350-1.150 years to capture 175 cm. The height descended again at the beginning of the industrial era (125 years ago) and the men of that time measured 170 cm. Current Americans are not much higher. |
How many of us are in Euskal Herria? Throughout history, the Basque Country has experienced important changes in its population. To see that this is so, just look at the last 150 years. In 1851 the population of the seven territories of Euskal Herria did not reach 900,000 inhabitants. Half of them resided in the territories that are currently part of the Basque Autonomous Community, about 300,000 in Navarre and the rest in Iparralde. At present we are 2 million more. The biggest growth has occurred in the CAPV, with a million and a half of the highest inhabitants, while it has been slower in the Basque Country North, with only 100,000 more inhabitants. In Navarre, finally, there are 240,000 inhabitants more than then. To explain the changes that have occurred in this time, it is necessary to take into account social and economic movements. XIX. In the twentieth century, many people left Euskal Herria and emigrated to America, while in the twentieth century, with the arrival of immigrants, growth was spectacular. This demographic explosion was especially evident in the ACBC: Between 1950 and 1975 the population went from 1,051,000 to 2,073,000 inhabitants, that is, in 25 years the population doubled. In addition, this doubling took place in the three territories. The industrial revolution changed the lifestyle and directly affected demography. However, the demographic evolution in Iparralde has been very different. While the Southern territories were receiving workers, the people of the North went to Paris and other industrialized countries, something that continues to happen. Thus, the population of Baja Navarra and Zuberoa has been losing since 1851, with 20,000 and 9,000 less inhabitants, respectively. |
Dispersed throughout the world, to what extent?
The distribution of human beings on the terrestrial surface is uneven, in some places it accumulates and in others, practically no one lives. The areas with permanent ice (North and South Poles), the great deserts (Sahara, Kalahari, Atacama), the high mountain ranges, some green deserts of Africa and Amazon are unpopulated places. Despite this, there is a great difference in human density: 75% of the population is concentrated in 10% of the floating lands. Most of the population (90%) lives in the northern hemisphere, 80% above the Tropic of Cancer and 50% in latitudes between 20-45º N.

As for the rest of the continents, Africa is not very populated either, nor America, and with the exception of some parts of Europe, it cannot be said that this continent has a high density. Finally, the density of Oceania in general is very low.
In view of the location of human groups, it is clear that the climate has a great influence; the human being, in addition to choosing the most appropriate or sustainable place for himself, must also be suitable for agriculture and livestock. That is why he has chosen the coasts and margins of the rivers. However, the excessive growth of the population and the change of lifestyle force human beings to occupy places that would not be adequate before.


Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia





