Published a distribution map of dark matter
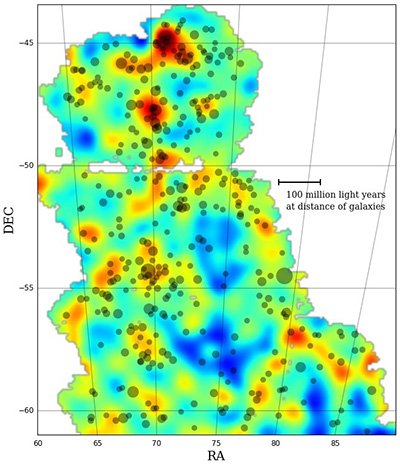
The Dark Energy Survey has just released a map in which dark matter is accumulated in the Universe and where it is not. The distribution map has been completed with a 570 megapixel superaccurate digital camera. In fact, although dark matter is directly invisible, astronomers are able to recognize it because its gravity reveals the light of distant galaxies, a phenomenon called gravitational lens. “We have measured tiny distortions in the images of about two million galaxies to create this map,” said research manager Vimu Vikram.
According to the researchers, the information received conforms to the predictions made so far on dark matter. According to these hypotheses, dark matter is one of the main engines of large-scale cosmic structures, as the map shows that the high density areas of dark matter are aligned with galaxies and galaxy clusters.
By completing the distribution maps of dark matter, the ultimate goal of the project is to measure the role of dark energy and hence its name. This type of energy has been proposed to explain the accelerated expansion of the universe, but it is still completely unknown.
Several international organizations participate in the Measurement of Dark Energy project, located at the Intermaricano Observatory in Chile, on Cerro Tololo. The map, first result, has been presented at the annual congress of the American Physical Society. At the moment, he receives only 3% of the universe area they want to explore until 2018.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian











