The human unconscious in virtual characters

The new system measures a series of parameters of human physiology that, in real time, are incorporated or incorporated into characters created by computer. Created by a group of researchers from the University of Barcelona, The Visual Computer, among others, has realized this.
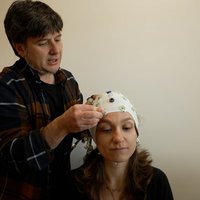
By placing a set of wireless devices and sensors in the human body, this system measures the person's current heart rate, breathing, and galvanic (electrical) skin response. The data is processed by a software that allows you to control the behavior of the virtual character sitting in a salon.
The character gives an answer to each of the physiological parameters mentioned. Breathing is related to the movement of the breast (excessive movements for better separation), the heart rhythm is reflected in the movement of the feet of the protagonist of the virtual world and the galvanic response on the face.

The challenge of researchers is clear: “We unconsciously seek that human beings may have a more intense relationship with certain elements of a supposedly virtual environment. In addition, each person’s physiological responses to visible virtual reality are the only ones that affect this issue.”
After measuring the parameters mentioned to several people, the researchers performed a kind of experiment. In fact, they wanted to check if they had some “preference” regarding the virtual characters (i.e., their direct representatives) that showed the same parameters as yourself. The result was negative.
“They didn’t know what we were observing, nor what each person’s character was, but they didn’t choose them,” they say. Surely other factors influenced this decision, such as the appearance of the characters or their own staging position. These factors remain stronger, immediately absorbing user attention.” The team has now shown its intention to deepen and further investigate this issue.
Looking for realism
Among other things, when they embarrass us, when they are frightened, the heart rate accelerates, while nervousness makes us tighten our breath. These processes are often unconscious, but our body sends clear signals. Thanks to the new system, all this can be seen clearly in the virtual character that represents us.

In short, a form of representation of the human unconscious through virtual characters is what the Barcelona group proposes: “the incorporation of these subjective situations of the human body into an imaginary reality would reinforce the realistic vision that each one has of that world. And in general, the same connection between human beings and this virtual reality would be tightened.”
In virtual presentations or video games we know characters that have a physical or voice appearance similar to the user, for example. And, to give more realism to the virtual world, the contribution of the new system can also be significant. Beyond leisure, it can also have applications in the health sector, “in rehabilitations, for example, it can help to arouse the interest of patients when performing certain actions”.
Published in 7K.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian