Resberatrol, therapeutic force of wine

The amount of surface resveratrol of the grape depends on several factors, including grape variety, geographical origin and fungal infections. In addition, the time of contact of the wine with the skin of the grape during the fermentation limits the concentration of resveratrol of the wine, so the white and pink wines have a concentration lower than the red ones.
In any case, to discuss the therapeutic capacity of resveratrol, knowing its concentration in food is of no use. The important thing is to know the concentrations obtained in blood after the intake of these foods. In relation to the latter, in a study with healthy volunteers, the absorption of 25 milligrams of oral resveratroles was analyzed. And the results indicate that, although the amount absorbed is relatively small, resveratrol was able to cross the absorption membrane and pass from the intestine to the blood, which in the future opens the possibility of applying resveratrol orally.
French paradox French paradox
In 1992, there was an interest among scientists to investigate the benefits of resberatrol in health. Then, Siemann and Creasy determined for the first time the degree of resberatrol of black wine using high resolution chromatography (HPLC) and saw that it could explain the "French paradox" (French Paradox). According to the French paradox, the fact that in France the mortality rate for coronary artery disease is lower than in other countries is due to a higher consumption of black wine, despite the fact that the French have a diet abundant in saturated fats and burn much.
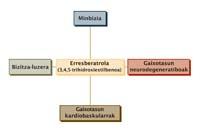
Since then, several studies have shown that resveratrol participates in mechanisms related to cardiovascular diseases and suggest that it can have a protective function in the cardiovascular system. In addition, during the trials carried out in cultural and animal cells, participation in other processes, such as the inhibition of the development of cancer, the prevention or treatment of inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases and longevity, has been observed.
It is clear, therefore, that the name of this polyphenol can be read or read in the reports of scientific projects by more than one scientist from around the world. The aim of this article is to present scientific evidence indicating the therapeutic capacity for each of them to draw their own conclusions.
By the heart

In addition, they have shown that resveratrol is capable of inhibiting platelet aggregation and causing vasodilation, so they consider that it can be effective in preventing occlusion of the coronary arteries and the central arteries of the brain and in decreasing blood pressure.
Ability to prevent cancer
The carcinogenic capacity of many compounds appears after their metabolization, that is, for these substances to be carcinogenic it is necessary that some enzyme of the Cytochrome P450 group activate them. Because resveratrol, reducing the expression and activity of these enzymes, prevents the formation of carcinogenic compounds.

In addition, resveratrol participates in the regulation of the life cycle of cells, avoiding mutations that can cause death or cancer in normal cells and inhibiting the death, growth, angiogenesis and metastasis of cancer cells. Likewise, the anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol inhibits tumor invasion.
In vitro experiments have shown that it is effective to inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells such as lymphoid cancer and myeloid, multiple myeloma, breast cancer, prostate, stomach, colon, areko and thyroid, melanoma, epidermoid carcinoma of the head and throat, ovarian carcinoma, and carcinoma of the cervix.
Resveratrol seems to help not only prevent cancers, but also to live longer. In fact, it has been shown that the consumption of resveratrol prolongs the life of worms C. elegans and fruit fly D. melanogaster. This effect seems to be due to increased enzymatic activity called sirtruin. In addition, according to studies published in prestigious journals Nature and Cell, resveratrol, activating sirtruins, increases energy expenditure and protects mice fed with a diet rich in fat from the risk of diabetes, obesity and hepatic degeneration. Finally, it has been detected that sirtruin activators can be useful to prevent neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (let's not forget that currently the incidence of neurodegenerative diseases is very high).
A powerful future
In light of what has been seen so far, the therapeutic capacity of resveratrol can be evident in the future. However, it should not be forgotten that in the aforementioned researches -- in cell cultures and in species of lesser rank than the human -- there have been used much higher concentrations than can be obtained in the human being orally, so we are still at the beginning of a long way.
However, with the concentration of resveratrol in blood after the ingestion of a glass of wine, scientists have been able to achieve therapeutic effects, although in vitro. For example, it has been possible to increase the activity of the enzyme eNOS, responsible for the synthesis of nitrous oxide, causing a decrease in blood pressure, which is very beneficial for the cardiovascular system.
It is evident, therefore, that the data give us reasons to be optimistic. In this regard, David Sinclair, a researcher at Harvard University who has participated in the works published in the journals Nature and Cell and who has blind faith in the power of resveratrol, has created the biopharmaceutical company Sirtris Pharmaceuticals. The aim of the company is to synthesize new formulations that can be taken by activators of sytruins, such as resberatrol, and orally.

Among its patents, the formulation of resberatrol SRT501 stands out. The SRT501 has a degree of stability and absorption much higher than the formulation so far, allowing higher concentrations of drug in the blood. To measure the efficacy and safety of SRT501, a clinical trial was conducted with 85 healthy volunteers and one with 90 diabetics. In fact, the results of these clinical trials show us whether the data obtained so far in vitro and laboratory animals can be extrapolated to the human being.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian











