Woman who knows no fear

S.L., 44, is one of the few people in the world with almost total injury in the two parts of the cerebral amygdala. As a result of this injury, the woman is characterized by not feeling fear, not knowing that emotion.
“Survival is the essence of fear and the amygdala helps us avoid situations, people and objects that endanger our lives,” summarizes the head of the recent research carried out at the University of Iowa. “The analyzed patient has no friends. And, therefore, it has no capacity to detect and avoid risk. Their survival is quite striking.”

The researchers released the case of S.M. A few years ago. The woman has a degenerative cerebral disease called Urbach-Wiethe, unusual, which aroused the interest of neurologists. The injury of the amygdala, caused by the disease, has had important consequences in the daily life of the woman.
Last year, for example, researchers at the California Institute of Technology discovered the presence of personal space in the brain. The personal space is a space of protection of individuals in their environment. When someone enters this area, the person feels uncomfortable — depending on the situation and the person who approaches the field has different dimensions. Well, the researchers saw that S.L. He does not feel fear on the faces of people. What’s more, he behaves too “friendly” with people he barely knows, overcoming his personal space.
Now, Iowa researchers have been the ones who wanted to continue studying the case of S.M. Their findings provide new information about the relationship between the brain and behavior. The results have been published by the journal Current Biology.
Appearance of almond
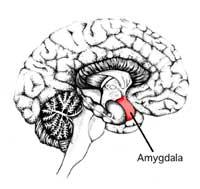
The amygdala is a mass of gray substance in the front of the temporal cerebral lobe in the form of almonds. Check all the information that reaches the brain through the senses to quickly detect anything that can affect our survival. According to neurologists, “when detecting risk, the amygdala organizes a quick response from the whole body to get away from it, which increases our chances of survival.”
The researchers wanted to analyze how S.L responds. Faced with multiple situations: snakes, spiders, “bewitched” houses, horror films, or, among others, traumatic experiences lived by the patient. For three months he carries with him an emotional computer journal to make known his experiences of the day. And they also made him comply with a questionnaire on the different perspectives of fear
S.L. He had no feeling of fear, in no case. “We have found that he is able to feel loneliness or sadness and other emotions. However, he does not feel panic, although we know that he has suffered a series of traumatic experiences that have endangered his life. Therefore, we have clarified that the amygdala is decisive in creating fear for both us and other animals.”
They say this discovery can help find new treatments for people with post-traumatic stress and other serious anxiety situations.
Published in 7k
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian











