Noise: More than annoying
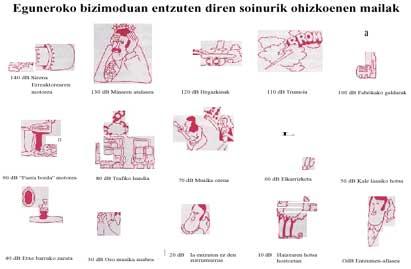
One of our most wicked enemies or enemies is free, fleeing the plot. Walk through the streets of the Basque capitals and villages, accessing offices, workshops, factories and houses. What is that bad character? Noise. If anti-noise or noise regulations and regulations were applied, many Basque companies (about 80%, according to some sources) should be closed. This shows the importance of the problem.
The noise has a bad reputation, but are there reasons to justify that bad reputation? If we attend to a report prepared for the European Economic Community, there is no doubt: It generates 70,000 annual workplace accidents in Europe, is responsible for 15% of lost hours and 20% of psychiatric treatments. And to put an end to the figures, in different European countries, local social security, up to 20% of budgets, dismisses the victims of noise.

In Europe one in three workers withstands excessive noise, e.g. More than 85 decibels for more than six hours a day. In France, for example (55 million inhabitants), 185,000 professional deafness is generated annually, each of which generates the company an expenditure of one million pesetas. The previous figure was lower, but today experts estimate that in shrimps that have to endure 85 dB for six hours a day, one in eight will suffer some ear disease and some will have it forever.
The sectors most affected are those who work in the street: construction or construction workers, public works, who absorb their own noise and traffic generated. The 31 leased from these sectors are forced to withstand noise levels about what the International Labour Organization considers "risk limit". It is followed by smelting and metallurgy, with 27% of workers affected, followed by the transport and textile industry, with 25% and 17% respectively.
However, there are very different noises and noises. Explosions of a pump, e.g. (because the noise is temporary) can cause temporary hearing loss. Between attack and healing there must be absolute silence. Compensation of 10 minutes over 100 decibels requires a silence of approximately 100 minutes.
Otherwise, "hearing fatigue" may appear. Hearing loss occurs when the noise level remains constant at 85 decibels for years or months (depending on the person). When the 15,000 eyelash cells the newborn baby has in his inner ear are destroyed and cannot reproduce, its destruction produces deafness, in many cases deep or total deafness.
Future ear medicines
Ten years ago we barely knew the functioning of the inner ear and five years ago we did not know the neuroactive substances that lead the communication between the ear and the brain. But as studies and research have evolved, researchers now have more than ten neuroactive substances in their hands, with biochemical, pharmacological and other properties in cochlear physiology.
At the moment it is only a beginning: in the future (perhaps in less long term) will appear medicines and treatments that resist the aging of the ear; able to relieve the auditory tiredness and to cure achufenos, buzzes and annoying noises for the delicate ear.
As a series of paths or vestiges that within a few years can achieve success. For the moment, the most hopeful looks like guatanato. This amino acid would behave like a neurotransmitter when the transmission of the auditory message does not work between the eyelash cells of the cochlea and the fibers of the auditory nerve. But guatanate can also be toxic to injuring hearing neurons. In the future it will be the doctors who will clear the matter.
On the other hand, in the city of Seattle, in the US, a group of university students have discovered that, after an acoustic trauma, they are able to reproduce the eyelash cells of the chicken cokeel. If we would be able to understand this process and have brought ourselves to the case of man, the regeneration of the inner ear would be possible. Or a transplant to the human being. Deep deafness would not be an insurmountable problem in the future.
Other negative aspects of noise
The Netherlands found that drug use in noisy areas was much higher than in quiet areas. For example, the number of prescriptions for anti-hypertension drugs grew as noise increased in the Amsterdam airport area, in areas with levels of 78 decibels. And the same thing happened with sedatives and sleeping pills.
In London it has been shown that healthy young adults who were at very high sound levels of 0.6 seconds duration every 22 seconds increased rates of cholesterol and stress hormone. These human caves were completely normalized with a half-day silence in voluntary experiments. However, in German workers between 30 and 40 years old, if one of the two days is put to the sound levels of traffic in house acts, it has been observed that their blood pressure rises much more than in other workers who work in silence (relative).
The body cannot get used to aggression or noise. In addition to the psychosomatic diseases that produce noise, are known as office vertigos: itobeharras, astenias, etc. Some London doctors came to this diagnosis for a group of secretaries who suffered a constant traffic noise of 76 decibels, when this pathology appeared in 25 secretaries of a new central office tower.
Each of us reacts differently to sound. It is impossible to know how far you can overcome. Today the youth usually act in discos more nervous and aggressive than when the orchestra played much lower. An old musician says there are more fights, more sessions and more angry than before. And, to a large extent, they are due to noise.
Traffic noise is supported much better by closing all windows. But what to do in summer? Let people who think they are not affected by noise test: after working 8 hours high, they will take the pulse and see the heart give 10-25 beats more than normal per minute. We got there with the noise.
And the same goes for those who believe that sleeping without noise or noise is the same. Noisy circulation reduces blood flow during sleep up to 70%. This is the result of research conducted on people living near the airport.
Children, the most affected
Although no one is yet verified or coded, noise is a threat to our children. In Japan, the issue has been addressed in the vicinity of Osaka airports and they have reached this conclusion; when the mother has spent her pregnancy in a quiet place, the children do not wake up with the planes. However, by passing pregnancy in a noisy place, newborns cry when they say goodbye.
Children living in very noisy environments, in order to properly develop their capacity, are not able to receive noises and their sleep is not adequate; they do not recover at all. Children who live in continuous noise (traffic, radio, TV, appliances, washing machines,...) learn to speak more slowly than children in rural settings.
We should also talk about the noise of schools (it would be assumed why there have been misunderstandings of many), or of bars because more than 60 dB can cause hearing impairments), etc. To achieve a better integral development of the child would need sound installations.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian











