The ozone layer hole decreases and divides
Since 1979, NASA and the U.S. Ocean and Atmosphere Administration have analyzed all ozone layer movements. The hole has been stable in the last 6 years, with a width of 24 million square kilometers, but in the last month there have been unprecedented changes.
In early September the hole changed from shape to elongated. In the last two weeks, in addition to the continuous reduction of the hole, up to 2 million kilometers wide, it has been divided into two sections. One hole has moved to Africa and the other to South America.
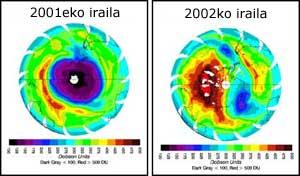
All these changes in the hole are due to atmospheric waves. These waves are responsible for the changes of time on Earth and also affect the high atmosphere. This year the influence of the waves has been greater than in recent years, which has resulted in the warming of the stratosphere.
Stratosphere warming reduces the influence of ozone perforating gases by not generating the ice particles needed to react with ozone. However, experts have insisted that all this change is only a temporary effect. The change in trend of atmospheric waves will alter the appearance of the ozone layer, and the hole will continue as long as there are gases that destroy ozone in the atmosphere.
To see the ozone hole changes click here
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian