If you don't hear well...
Why is hearing lost?
Hearing loss is defined as decreased hearing acuity or listening ability of a person below normal level. And the causes are many and very different:
- Family history, viral infections of the mother during pregnancy (rubella, HIV, etc. ). ), cranial malformations or premature births (if the weight of the newborn is less than 1,500 kg) are sufficient reasons to prevent some of the parts and mechanisms involved in the complex hearing process from the very moment of birth. And that, of course, generates hearing problems.
- Later, persistent serous otitis or meningitis can significantly reduce our ability to listen.
- Over time, as a person ages, hearing also decreases, especially from age 60.
- Presence of strong blows on the head and in areas with high noise (working in noisy areas without plugs, listening to music at high volume, etc.) are very important risk factors to consider.
Last minute treatments
Interestingly, older people adapt better to hearing loss than to visual loss. If someone does not see well go immediately to the eye doctor, who puts him or her antieye, but the same does not happen with hearing problems. A survey conducted among the elderly showed that 6.2% of the elderly have hearing aids, but half of them do not use, because they are uncomfortable, expensive, still have defects and, ultimately, because the user does not perceive a significant improvement of the prosthesis.
However, the latest generation hearing aids (known as analog hearing aids) have a greater sensitivity to the sound ahead, and thus the person listens better in the direction they look. In addition, these new prostheses are able to differentiate them between noise and speech and eliminate the beeps that occur when chewing or talking on the phone.
In addition to being better, more sensitive and strong, producers have tried to make smaller prostheses, until they become almost invisible. There are rear ear prostheses placed inside the canal (those placed in the ear canal are usually the size of a nail) and attached to the arms or temples of the glasses.

However, the most significant progress has been made in cochlear implants. Through an operation, the specialist applies to the patient a device or device in the inner ear for the performance of cochlea functions. The implant collects acoustic signals and converts them into electrical signals that excite the auditory nerve. Subsequently, these electrical signals, as if they were nerve impulses, are brought to the brain for interpretation.
The results can be surprising, especially among people who have already developed their language skills. In addition, it can be a good opportunity to improve communication between deaf children from birth or very early cut children. After surgery, however, rehabilitation is essential: After 3-4 weeks, 80% of what many patients call comes to understanding without reading on the lips of the interlocutor. The sounds are slightly metallic, but the affected can recover much of the ear thanks to the implant.
And you, reader, are you losing your ear?
- Even if you are attentive, you cannot understand all the words of a conversation. You follow the thread, but you lose important information.
- The sharp sounds are the ones you lose most unconsciously.
- You become less involved in conversations with fear of misunderstanding or acting out of time.
- Those around you report that you have very high TV or radio.
- Sometimes you don’t react by ‘hearing’ your name, phone sound, alarm clock, or home bell.
- Your voice is also increasingly used in normal conversation.
Listening skills can be measured and although tests are many, audiometry is essential. It is performed in the soundproofed room and the audiometer emits certain frequency and intensity sounds so that the patient can identify them. This is how the specialist can know which sounds are heard and which are not.
However, as sound waves are also transmitted through the cranial bones, in addition to the audiometry aerea is also performed bone. And the sound audiometry is completed with a vocal audiometry in which phrases, words are made to see how it separates them.
Types of deafness
The causes of deafness or hearing loss can be multiple, as we have seen before, but depending on the structure of the ear that affects, they can be classified into two main groups: the perceptive or neurosentsorial transmission hypoaccuses or hearing loss.
Transmission or conduction hearing loss
In these cases the problem is in the outer and/or middle ear. Sound waves do not reach the inner ear correctly and are not heard with the proper intensity. Recorded sounds are the most affected.
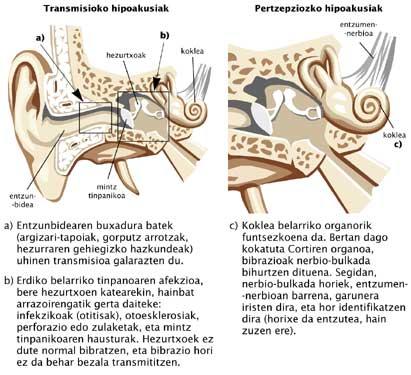
In these cases the alteration is due to an injury to the inner ear, auditory nerve, or sound detection area in the brain. Infectious, inflammatory, toxic and degenerative processes may be behind the injuries of these delicate structures. Sharp sounds (for example, bells or phones) are the least heard, but it is common that they do not understand well what is heard in the same way. Normally the lesions are irreversible and the only solution is to use prostheses that amplify the sounds. If the results are not satisfactory despite the use of the hearing aid, the only appropriate alternative is to try cochlear implants.
How to detect that the baby does not listen well
Parents are essential to detect possible hearing problems of the baby. Immediate onset of treatment prior to diagnosis can prevent the most serious consequence of the problem (prevent the child from talking). It is best to treat it before six months, but unfortunately many cases begin to diagnose after two and a half years. Hurry up!
- The child does not wake up with loud sounds (cowbell, bells, etc. ). ).
With 7 months
- Don't try to know where the sound comes from.
- Listen to the voice of people you know and don't react.
- He does not realize that people have approached and therefore does not move his eyes in his search.
- It does not foolish, nor imitates sounds or sounds.
- It does not react with the bell or sound of the phone.
- He does not respond with his name, nor do the noises or noises produced outside his field of view frighten him.
- He doesn't start talking, he doesn't say words.
- You cannot say simple words or very simple phrases.
- It does not answer extremely basic questions, except for gestures of help to interpret them.
- The child does not see what he is talking about.
- Their language development is not normal or suitable for their age.
- When you say loose words, you usually shout.
- When asked a question, it is very common to answer “what?”.
- Usually put television or music very high.
- He is introverted, silent, he is in his world. You find it hard to relate to other children.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian