Hypertension in the blood
Hypertension is called a high amount of blood pressure. But, of course, that requires that we previously know when the figures are “normal”, because not all people have the same stress figures within normality.
Arbitrarily, the World Health Organization demands two conditions for the definition of hypertension: systolic pressure Ž160 mm Hg and diastolic pressure Ž95 mm Hg, always in adults.
And what are those figures?
Systolic pressure (or high, as the simple people say) corresponds to the contraction of the left ventricle. This figure indicates the time when the blood begins to pass through the compressed artery.

Diastolic pressure (or baXua) corresponds to cardiac rest. When we begin emptying the tension intake device, the artery returns to its normal state and the blood begins to circulate normally until we hear no noise. At this moment the diastolic figure corresponds.
At this point we could say almost so many opinions. That is, a lot of wrong or false ideas, beliefs or beliefs about these figures is huge. I will mention two of them. They are those who do not have great scientific reasons in their base, but in practice they are fulfilled quite well.
- Before putting the number 1 to the figure that marks the decade of the age of the person and the number so created would mark the systolic that should have said person. For example, a 28-year-old, 12-67, 16-year-old.
- The diastolic figure would be half plus one of the systolic. Following the same examples above (12:2) + 1 = 7 and (16:2) + 1 = 9.
Therefore, according to the two previous false laws, the normal stress of the 28-year-old would be 12/7 and that of the 67-year-old 16/9.
What is the importance of hypertension?
Hypertension represents between 15-19% of the population, that is, one in every 5-6 people has a high tension. However, 40% do not know that it is hypertensive. Of the 60% who know they are hypertensive, half do not go to the doctor. Therefore, do not take medication or treatment. And finally, only half of the people who come to the doctor are properly treated.
What are the factors that cause hypertension?
- Weight. It is shown that obesity leads to hypertension.
- Sex. Between 45 and 50 more years in men (2:1). From this age the relationship is inverse.
- Sedentarism
- STRESS. More in developed countries than in primitive peoples.
- Salt consumption
- ALCOHOL. 50 grams of alcohol are allowed daily. From there, alcohol is considered a risk factor.
- Hormonal contraceptives (in women) and hormonal causes in menopause.
- However, 90% of all arterial hypertensions are of unknown etiology, called essential hypertension.
How to take tension?

The patient must be completely calm (both physically and psychically). If possible, you should be lying on a bed 5 minutes earlier, in a quiet room, without smoking. (It is obvious that this is practically never true).
Place the arm without clothes to the shoulder so that the sleeve can be placed well and the clothes do not press on the artery of the arm. The arm must be supported.
Normally the tension is taken in the humeral artery. Therefore, the rubber bag of the hose will be placed on the front of the arm, leaving its lower edge above the elbow at a minimum distance of 2 cm.
Systolic voltage is determined first by palpation. For this purpose, the manguita swells quickly until the pulse of the radial artery disappears. Then it empties slowly (10 mm Hg every 2-3 seconds) until the pulse returns, when it gives us maximum blood pressure.
Then the hose is completely emptied and the tension is taken again, this time by auscultation. The heartbeat of the humeral artery is located in the crease of the elbow and is where the stethoscope is placed without excessive pressure. The cuff is switched back to a pressure of 20-30 mm plus Hg than the systolic pressure previously found with the palpation method. Then it begins to slowly dislodge until you hear the first sound (systolic blood pressure) and continue emptying to determine diastolic blood pressure (when you stop hearing sounds).
The point to consider is the arm in which, normally in the right arm, figures of 2-10 mm Hg are obtained higher.
Finally, do not forget the possible failures in the voltage intake (due to the apparatus, noise in the environment, etc., produced by the person who takes the stress, state of nervousness of the patient, etc. ).
Characteristics of the disease
The symptoms are scarce and scarce, and there is no reason to call hypertension “silent killer”.
On the other hand, symptoms are not excessively specific: headaches (55%), dizziness (50%), cramps (44%), nervousness (40%), palpitations (37%), vision problems (36%), fatigue (30%), precordial compression (26%) or sweating (13%) are the most common.
When is a hypertensive person?
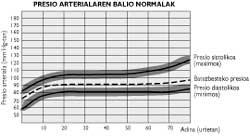
Its voltage figures are higher than 160 mm Hg and 95 mm Hg in three consecutive sockets, leaving one week between them. See attached image.
When to start treatment?
Eye with diastolic or low blood pressure and mm in Hg
The treatment should be:
- Easy to understand for the patient without complications.
- easy to kunplitz: for example, taking medications at meals.
- effective (under medical control).
- controlled (taking voltage sporadically).
- adapted to the conclusions obtained.
Very varied measures can be proposed, but first of all it is necessary for the sick to have clear the importance of the change of life in the mind.
- Cigarettes. Less than 6 a day. Better not smoking anything.
- Alcohol. Less than 20 g/day.
- Salt. Use little salt in food preparation and do not use saleros on the table.
- Meals. You have to control and/or discard the fish and frozen meats, the sweets in general ¡ojo! ; envelopes; snacks in general; anchovies; bacon; cheeses; spinach; sausages; ham; preserves and tissues.
- Weight control
- Drugs. They are used of different types, adapting to each case: - Diuretics: for the kidneys to expose more water and salt - Beta-blockers: to relieve the work of the heart - Drugs that reduce peripheral resistance found in the blood.
Treatment of treatment Treatment | Age 40 years old | Age 40-59 years old | Age 60 years old |
Essential Recommended Optional Useless | 130-110 105-100 95 90 | 130-115 110-105 100-95 90 | 130-120 115-110 105-100 95 |
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian











