Technical service classroom at the Arrasate Polytechnic School
1994/10/01 Arrojeria, Eustakio - Elhuyar Zientziaren Komunikazioa | Azkune Mendia, Iñaki - Elhuyar Fundazioa Iturria: Elhuyar aldizkaria

So far Production Management in companies and Manufacturing itself have been independent areas. Production management, orders, stocks, raw materials, etc. taking into account the manufacturing plan. The manufacture, subsequently, took this plan and carried it out in the most appropriate way possible, attending to the degree of occupation of its machines, breakdowns, etc., but often it was not suitable to the management of the Production.
Technical service in philosophy, production management uses up-to-date manufacturing plant information and makes the right decisions at the right time.
The Arrasate-Mondragón Polytechnic School, the result of the four-year work of its teachers and students C.I.M. has set up a room.
Technical service Classroom objectives

Technical service prepared at school the main objective of the classroom is didactic. The classroom will be used mainly for the realization of the practices and will work, among others, the following areas and topics:
- Electronics: automatons, sensors, controllers, actuators, identification systems, local networks, artificial vision, robotics, control and inspection of systems, numerical control of machining by chip start, etc.
- Computer: local network management, PC and mini-computer programming, database processing, etc.
- Production: production management, quality management...
In the practices of these areas students will carry out projects with the help of teachers.
Technical service general classroom structure
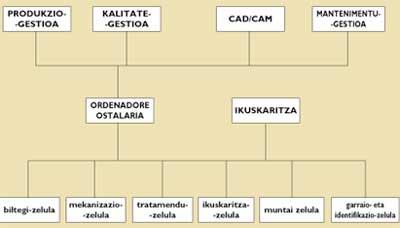
Technical service according to the general structure of the system, in the room there are five cells physically connected to each other by conveyor belts. The general structure of the classroom can be seen in the upper organizational chart.
In this general structure of the classroom, the structure of information and automation make up the pyramid. In the internal level there are sensors and actuators, in the first level automatons, numerical controls, etc., in the second cellular control, in the third control in plant and inspection and above all, in the vertex, global management.
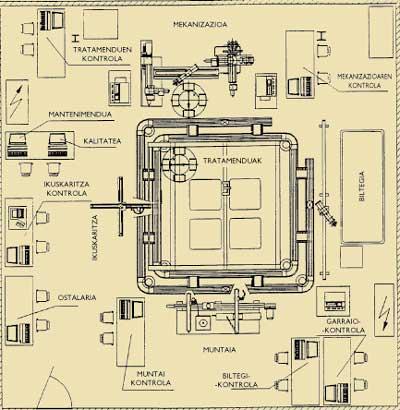
Technical service The arrangement of the different elements within the stay can be seen in the image of the next page.
Operational

It is part of the manufacturing order, references to produce in it, quantity produced, time, etc. It is determined. The system will sequentially prescribe manufacturing, taking into account, as far as possible, the availability of pallets with the necessary tools.
Once the manufacture of a reference is organized, it will be carried out sequentially performing a series of tasks in each cell. The final work of the last cell (usually quality control) involves the entry of the finished product into the warehouse.
Each of the jobs to be performed in each cell will end with other jobs (sometimes parallel and synchronously) of the previous level performed by cellular elements. Once each of the lower works has been completed, the elements of the cell transmit information to the host computer to make the appropriate decisions.
If alarm is performed at the lower level, it is immediately transmitted to the cell control organ. The cell control organ will determine whether the cell should remain or whether the product will continue to work.

If the cell stops, the information is sent to the host computer of the plant. This will determine the continuity or modification of manufacturing. It will also continue to treat manufacturing orders that do not require work in the affected cell.
In any case, the reason for the alarm and alarm will be recorded both in the cell organ and in the host computer of the plant to be taken into account for preventive maintenance.
Control and management system
Technical service Due to the didactic objective of the classroom, the practices can be carried out at three different levels: at the plant level (that is, with all the cells working), at the cellular level (with the elements of a certain cell running) or at the individual level of the element (with an element of a certain cell running).

To do this, each cell has its operating autonomy and its own personal computer. Thanks to personal computer software, the cell can operate at three different levels.
At the individual operating level, a certain element of the cell (numerical control, automaton, etc.) emulates as if connected directly to the computer. This level of operation allows to improve the control programs of the different elements.
The work to be carried out by the different elements of the cell must be coordinated at the cellular level. These works are coordinated by the Petri network.

In plant level manufacturing, the different works to be performed by the cells are sequenced and simultaneous operations are coordinated in several cells in different references. Petri networks are used to coordinate and sequence the work of different cells. At this level of operation a manager can see the status of the plant at any time on the screen.
Brief description of cells
Transport and identification cell
The function of this cell is to transport the palletized parts to the rest of the cells. Take unworked parts from the warehouse and after completing all cycles in different cells transport them back to the warehouse. In principle the pallets are transported and in each pallet go the parts that make up the product.

This cell consists of computer, two conveyor belts and twelve pallets. Each pallet bears a label with the destination of the pieces, date, full tour, etc. The pallets are moved by friction on conveyor belts.
Warehouse
This cell has several functions. It takes raw materials out of stock, deposits the raw materials from the warehouse into pallets (so that the conveyor belts take them to the cells), takes the finished products from the pallet and deposits them in the warehouse, takes the finished products from the warehouse to the outside and performs the management of the products from the warehouse.
In addition to the warehouse structure, it has a computer and a robot with five levels of movement.
Machining
The machining cell aims at machining pallet parts. It consists of a flexible cell with lathe and milling machine that work with numerical control. In addition to the computer, it has a robot to load and download parts to the machines.
Due to the size and power limitations of both the lathe and the milling machine, it is not possible to machine parts of more than one measure, but this is C.I.M. does not establish any limitation to the didactic objectives of the classroom.
Treatments

The function of this cell is to improve the finish and appearance of the products. Computer, table loading and unloading robot, trays, temperature controller, treatment containers, etc. has them. This cell simulates treatments.
Inspection Cell
In this cell the quality of the treated parts is pre-machined and controlled. The parts are ripened on the pallet and conveyor belt. A camera controls the parts in size and shape. The parts are illuminated and the camera indicates whether it is either dimensionally or not.
Computer, camera, artificial vision system, etc. has them.
Assembly

In this cell the different parts that have been worked in the manufacture are mounted. In each pallet there are the parts to be assembled and the robot joins and joins the different elements of the assembly. Parts adjustment, screwing, etc. are performed. The screws have an extra feeder in this cell.
Technical service organization and cost of the classroom
The C.I.M. is completed thanks to 30 projects carried out in the last four years at the José María Arizmendiarrieta Polytechnic School in Arrasate, led by about 40 students by five teachers. Room. These projects have worked in different areas (computer science, mechanics, electronics, production, etc.) Computer Integrated Manufacturing has been launched this year in the aforementioned room. After teacher training, the Arrasate Polytechnic School has begun to teach students of this class.

They have needed an investment of 70 million pesetas (3 million pounds) and materials of 13 million pesetas (500,000 pounds), among others, and in their funding has participated the Basque Government.
Conclusions
Technical service It must be recognized that through the classroom a new vision has been given to engineering studies. It takes a more global view of the company and from the different departments of the School has fostered the interdisciplinarity of teachers.
Classroom students also have more than one area in their projects (computer science, electronics, production, etc.) work and acquire a more complete practical training. Now they can complete the company automation. More than automating production and reducing costs, we are currently looking to control production management.

Gai honi buruzko eduki gehiago
Elhuyarrek garatutako teknologia






