High capacity small labels: RFID technology

RFID: Radio Frequency Identification in English, radio frequency identification in Basque. The name itself causes any type of object to be identified by radio frequency, by waves, that is, without direct contact.
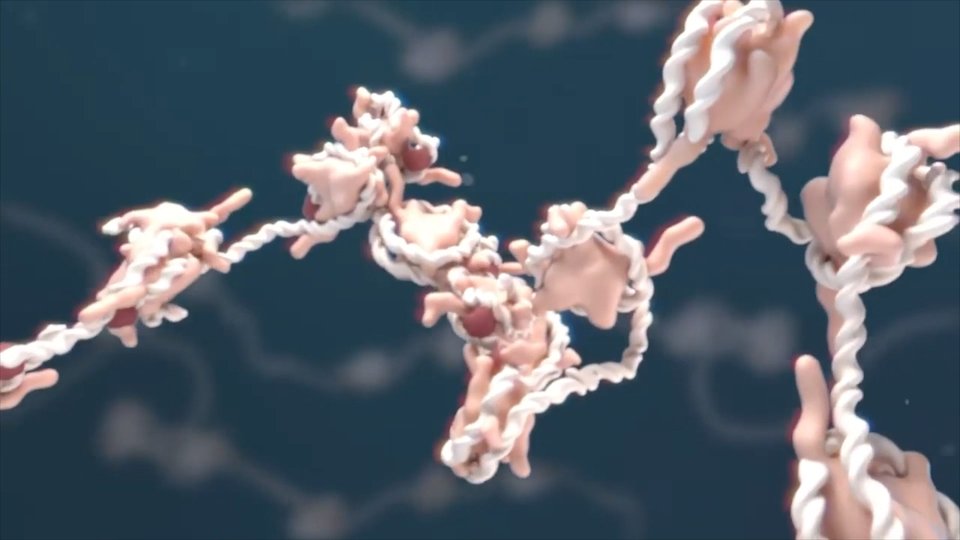
This system consists of two main components: The same RFID tag, with chip and antenna, and the RFID sensor-receiver or RFID reader. The reader is responsible for collecting, processing and processing the information sent by the label. The label can be like a sticker. It can be placed in animals, in people or in different boxes and products, and can give many data: name, characteristics, colors, customs, dates... It is a portable and powerful data transmission system.
The idea came about in the 1980s, when American researchers tried to develop systems of object recognition and analysis. However, they realized that this involved more problems and difficulties than expected, and thought it was better for the objects themselves to identify. In this way, RFID soon became a reality due to its ability to continue with mobile objects.
Types of RFID tags
There are two types of RFID tags in general: passive and active labels. Passive labels are very special, as they do not need any power supply, so they do not use any battery or battery. Therefore, to obtain the energy needed for response and data transmission, the small reading signals sent by the RFID receiver transmitter are used. That is the essence of the spiral shape of the RFID tag.

Passive labels, lacking their own power supply, have the ability to send a small number of data and cannot send them over long distances: From 10 millimeters to 5 meters. On the contrary, the absence of own power supplies allows to develop very small labels. Therefore, they can be placed under cover, in cardboard boxes or in banknotes. In fact, the smallest RFID tag that was on sale in 2005 was 0.40x0.40 millimeters and thinner than a sheet of paper, in one contact four. With this size they can be invisible.
Active tags, on the other hand, have their own power supply and are able to emit further and further data. The strongest can reach 10 kilometers. Memory and data storage capacity is also increased. In addition, active labels are safer in certain environments, for example at very high and low temperatures or near water.
But they also have disadvantages. Because of the power supply, they are larger than liabilities, but currently you can also find size coins. Also, the batteries are finished and then you need to change your own label or battery (some batteries can last several years). On the other hand, passive cards are cheaper, so today most are of this type.
Multiple applications
The small size of the cards allows them to be placed in the most hidden places and are portable. Therefore, they have many applications and are very practical, sometimes they are unbeatable and others quite arguable and unfair.

A clear example can be found in supermarkets. If you go to any shopping center in Euskal Herria, anyone can go out with a product that has bought and paid and start chistonar door detectors. This does not mean we have stolen something, but the cashier has badly removed or removed the RFID tag from the product. In fact, there are many products that have started to incorporate RFID in shopping malls, not only to report theft, but also for automatic product stocks, sales control or the availability of shelves and warehouses. Therefore, the RFID tag can replace the barcode system in the coming years, although for now it is somewhat more expensive.
In addition, the inclusion of the RFID tag on credit cards will allow us to make an automatic and lightweight payment through a detector without waiting queues. In Hong Kong, for example, on the Octopus card type, this system is now available. The European Union also intends to introduce RFID chips into the banknotes - rumors already say so -. This is apparently due to the counting, tracking and ease of payment of tickets. RFID is a huge system for this purpose. However, the system can be huge also to facilitate the work of thieves, through an RFID reader, since a thief can know at all times how much money a person has.
With RFID systems it is possible to conduct commercial research, track buyers and analyze consumer habits without customer consent.
Other applications of interest are intelligent traffic signals. According to forecasts, RFID chips will be installed in traffic signals and beacons in the coming years, and vehicles will have RFID readers. Readers will detect, understand and alert the driver by voice or holographic images projected onto the windshield.
Privacy in danger

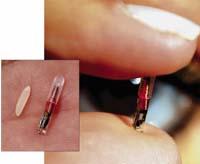
If one of the above themes seems taken from a science fiction book, it is no exception: vaccinations. The insertable RFID chips were initially designed for implantation in animals, but the possibility of incorporation into people is not excluded. Through them you could save medical records, avoid identity theft, control access to protected buildings or computers, etc.
The ethical legitimacy of these projects is not clear, but there is already in the market a chip that can be inserted in humans. A related curiosity: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) started in 2004 a study to decide the approval of the use of RFID chips in hospitals. And that organization approved the first chips that can be incorporated into humans: Manufactured by VeriChip and with a frequency of 132.2 kHz.
It is not questioned that these uses can generate benefits, but the possibility of restricting individual freedoms and attacking privacy should not be ruled out. For example, in recent times digital passports are at the top. For that can be a very serious and noteworthy case, how it develops.
There are two main types of digital passport technologies: RFID and SmartCard. The latter must be inserted into a special reader to be able to read it, such as coin cards. That is, in addition to the reader, physical contact is necessary to read the chip and obtain the passport data.
However, using RFID allows remote reading of data without authorization or physical contact, only an RFID reader is required.
Specifically, USA and other states have chosen this second for digital passports. They have no technical advantages over SmartCard. However, privacy can be a big risk, and anyone who can benefit from this technology can commit theft or targeted attacks.
Therefore, the debates and boycotts that have been generated around this issue are not few. We are faced with a conflicting issue and full of doubts, we will have to see what will happen.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian