Newly discovered New Zealand hydrothermal fireplaces

Hydrothermal chimneys are sources of hot water generated in terrestrial ocean bottoms. They are related to volcanic activity and are generated in the meeting areas of two tectonic plates.
The water previously submerged in the ground comes out again from the chimneys. The water is very hot and full of minerals, and when they come into contact with the cold water outside, they precipitate the minerals and create chimneys.
Scientists have discovered a very special ecosystem around chimneys. From this hot water there are microorganisms that capture energy and transform it, while these microorganisms are the basis of a whole food chain: worms, molluscs, crabs and many other living things around the chimneys. They all live thousands of meters deep, in all the darkness and withstand high pressures and temperatures.
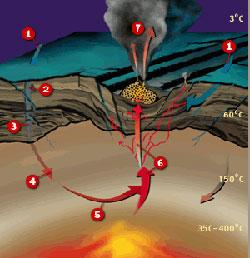
Since the first chimneys around the Galapagos Islands were discovered in 1979, similar structures and ecosystems have been found in all the Earth's oceans. The latest are those found recently in New Zealand. During the study of the submarine chain of the coast of the north island to the northeast, new chimneys have been found. Three new species of molluscs and unknown thermophilic microorganisms have been found in these chimneys. Therefore, they are more abundant and rich ecosystems than is believed.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian








