Wind profile
As the name suggests, the radar profiler makes profiles: above it gives a profile of winds that circulate at an altitude of up to 3000 meters, determining its direction and speed. This is the particularity of conventional radars used in weather that report aircraft, precipitation data or speed in the car.
Galernas forecast
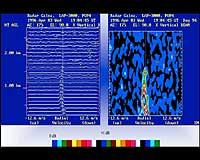
You probably won't remember it, but on February 7, 1996 a deep depression caused a strong galerna wind, with speeds of 125 km/h. Through the profiling radar we could see very well how the wind front approached the coast and how this forehead in altitude descended from top to top, reaching the height of the earth towards 7 in the morning. Profiling radar is an instrument used to know, predict and analyze violent weather events like this.
The radar performs wind measurements every 25 minutes, but in addition to wind fluctuations, it measures the temperature every 30 minutes. To obtain wind data, the radar antenna emits microwave pulses to the sky in five directions. A pulse is sent vertically, directly to the zenith and the other four cardinal points, with an angle of 15.5º. Changes in the atmospheric refractive index cause some of these microwaves to return to the antenna. Treating on the computer the frequency differences of the waves emitted and collected on the turn, represents the profile of the wind with the exact direction and speed of the wind. However, the interpretation and conclusions of these images and data are the work of experts.
They normally measure winds up to 3,000 meters of altitude, but vary depending on the conditions. To measure the temperature are used the waves collected by the radar and especially the acoustic signals emitted for it. The temperature is measured up to an altitude between 700 and 1000 meters.
Ozone research
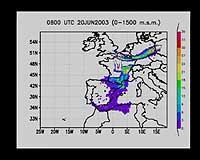
All these data are collected in the Basque Government's Directorate of Climatology and Meteorology and in the School of Engineering of the University of the Basque Country, in the Atmospheric Environment group. In this group, in particular, long-distance ozone transport has been investigated.
Since 1989 it was known that ozone bags were produced in concentrations higher than those due to local production. Data obtained through the radar profiler and transport patterns and weather routes have shown that ozone is transported long distance at high altitudes. Thus it has been stated that the ozone measured in the Basque Country in certain weather conditions has come from Brittany, in addition to what has occurred there. It has two routes: one of them is the current of air coming directly from Brittany and the other that enters through the valley of the Ebro after passing through the south of France and Tarragona. In both areas there is an increase in ozone.
Keep in mind that when ozone is in the upper layers of the atmosphere, it helps protect us from solar radiation, but in the lower layers of the atmosphere it is toxic and the inhalation of many ozone affects us. It is very important to know this transport.
Buletina
Bidali zure helbide elektronikoa eta jaso asteroko buletina zure sarrera-ontzian